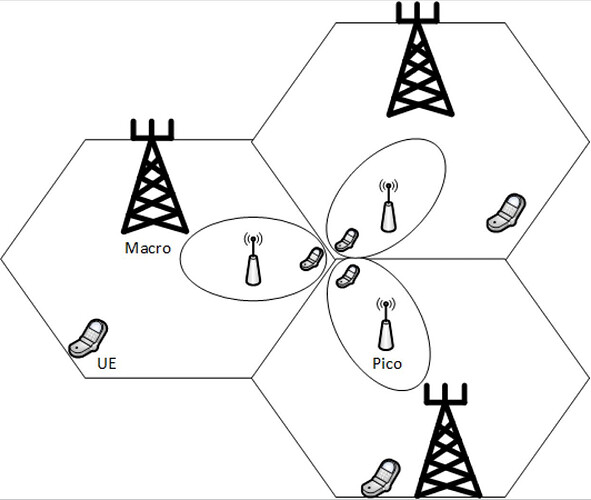
Comparing macrocells, microcells, and picocells in wireless telecommunications involves examining various aspects, including coverage area, capacity, deployment scenarios, and use cases. Here’s a comparison of these cell types:
- Coverage Area:
- Macrocell: Macrocells provide the largest coverage area among the three. They can cover several kilometers in radius and are typically used for providing wide-area coverage in urban, suburban, and rural areas.
- Microcell: Microcells have a smaller coverage area compared to macrocells, typically ranging from a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. They are often used to enhance capacity and coverage in areas with high user density.
- Picocell: Picocells have the smallest coverage area of the three, usually ranging from tens to a few hundred meters. They are deployed to provide coverage in indoor environments, densely populated urban areas, or to fill coverage gaps in specific locations.
- Microcell: Microcells have a smaller coverage area compared to macrocells, typically ranging from a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. They are often used to enhance capacity and coverage in areas with high user density.
- Capacity:
- Macrocell: Macrocells have relatively high capacity, suitable for serving a large number of users simultaneously. They are used for broad coverage and capacity.
- Microcell: Microcells have a moderate capacity, designed to serve users in specific regions with higher traffic demands.
- Picocell: Picocells have a lower capacity compared to macro and microcells. They are used to offload traffic from larger cells or serve localized areas with high user density.
- Microcell: Microcells have a moderate capacity, designed to serve users in specific regions with higher traffic demands.
- Deployment Scenarios:
- Macrocell: Macrocells are deployed as the primary cell layer for wide-area coverage, such as citywide or regional coverage.
- Microcell: Microcells are typically deployed to enhance capacity and coverage in areas with high user density, like shopping malls, stadiums, and busy urban streets.
- Picocell: Picocells are deployed in indoor environments (e.g., offices, airports, shopping centers) or areas with specific coverage needs, like small urban canyons.
- Microcell: Microcells are typically deployed to enhance capacity and coverage in areas with high user density, like shopping malls, stadiums, and busy urban streets.
- Use Cases:
- Macrocell: Macrocells serve as the backbone of cellular networks, covering large geographic areas and providing connectivity to a wide range of devices.
- Microcell: Microcells are used to alleviate congestion in busy areas, ensuring that users in high-traffic locations receive sufficient network capacity.
- Picocell: Picocells are used to extend coverage into indoor areas and small outdoor spaces, improving signal quality in places where macrocells may have difficulty penetrating.
- Microcell: Microcells are used to alleviate congestion in busy areas, ensuring that users in high-traffic locations receive sufficient network capacity.
- Interference and Frequency Reuse:
- Macrocell: Due to their large coverage area, macrocells may face interference challenges, requiring careful frequency planning and cell sectorization.
- Microcell: Microcells can use frequency reuse more effectively than macrocells, as they cover smaller areas and can reuse frequencies in a more localized manner.
- Picocell: Picocells can reuse frequencies even more efficiently than microcells since they cover very small areas and are typically deployed in locations with a limited number of users.
- Microcell: Microcells can use frequency reuse more effectively than macrocells, as they cover smaller areas and can reuse frequencies in a more localized manner.
LinkedIn: ![]()