Understanding the call flow is crucial for telecom enthusiasts.
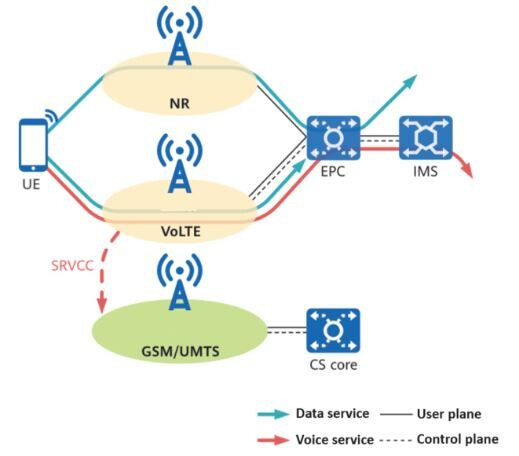
Let’s talk about the 5G Voice call in a NSA (Non-Standalone) network.
- The Call Flow in a 5G NSA Network
-
Phone is in 5G Coverage
Your device is in 5G coverage, but the core network is still LTE-based (NSA network setup).
The phone first connects to the 5G NR for data services (fast internet) but keeps using LTE for voice calls (VoLTE). -
VoLTE Setup on LTE
When you make a voice call, your phone uses VoLTE (Voice over LTE), which ensures high-quality voice calls over the LTE network.
The IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) is used to handle the voice call request, and your phone is assigned a bearer channel to maintain the call. -
Call Setup and Routing
The call is routed through the eNodeB (LTE base station) to the MME (Mobility Management Entity), which handles the session and mobility management.
Your call will also be coordinated with the PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function) to ensure the appropriate Quality of Service (QoS) during the call. -
Interworking Between 4G and 5G
In the NSA architecture, the 5G gNB (Next-Generation NodeB) provides enhanced data capabilities, but your voice call still runs on the 4G LTE network.
The core 5G network (5GC) handles data, while the EPC (Evolved Packet Core) manages voice traffic. -
Seamless Handover for Data
While your voice is handled by LTE, your device will benefit from the high-speed data provided by 5G when you use apps or browse.
This means you get fast internet for browsing, streaming, and more while your voice call happens without dropping quality.
LinkedIn: ![]()