-
My friend: Hi Ibrahim, I have a question for you.
- Me: Go ahead, please.
-
My friend: Last time we discussed about the 5G L1 acceleration but how can we implement the 5G L1 HW acceleration?
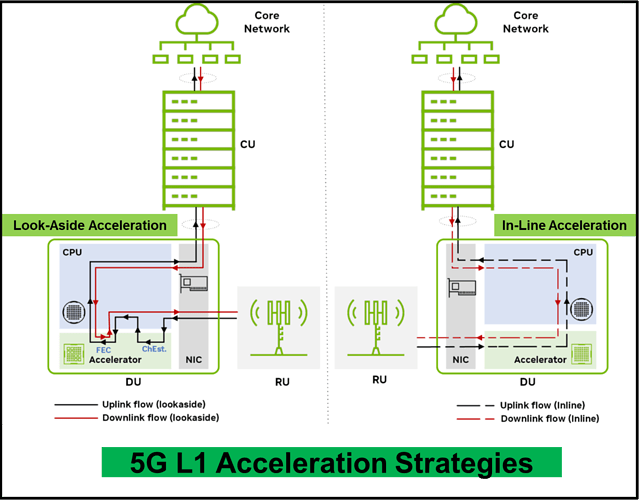
- Me: HW acceleration for 5G L1 can be done using two approaches which are Look-Aside and In-Line. And let me start with Look-Aside technique which is simply to offload selected key functions of the 5G L1 functions, for example, FEC (Forward Error Correction), from the COTS CPU to a separate card or integrated in the main chip with the CPU. So, the COTS CPU will still do most of the L1 functions, except the ones that will be done by the accelerator, in addition to L2 and L3 functions as well. The 2nd type is In-Line which is to offload most or all of the L1 functions to the accelerator card and leaves the COTS CPU to perform L2 and L3 functions only.
-
My friend: So, which technique is better?
- Me: This is a very difficult question to answer
 . However, let me explain the pros and cons for each solution, then we can decide. From system scalability point of view, in-line is a better solution as it will allow to scale L1 independently from L2& L3, and this is what we need as L1 processing scales with the increase of bandwidth and the no. of antennas connected, while L2& L3 processing scales with the no. of UEs, no. of connections and the traffic volume. So, using in-line solution, you can increase the no. of HW accelerators if L1 processing increased, and you can increase the no. of COTS CPUs in case of L2 or L3 processing increase, unlike look-aside solution which requires to increase the no. of COTS CPUs if any of L1, L2 or L3 processing increased as COTS CPU is handling all of them. Also, from capacity point of view, if we have huge traffic, then look-aside solution can be an issue as the data of the L1 selected functions will be sent back-and-forth to the hardware accelerator which will affect the processing time and hence can affect the latency-sensitive services, while in-line solution will be a better option. From energy efficiency, look-aside solution is more energy efficient at low-capacity sites, while in-line is more energy efficient at high-capacity sites.
. However, let me explain the pros and cons for each solution, then we can decide. From system scalability point of view, in-line is a better solution as it will allow to scale L1 independently from L2& L3, and this is what we need as L1 processing scales with the increase of bandwidth and the no. of antennas connected, while L2& L3 processing scales with the no. of UEs, no. of connections and the traffic volume. So, using in-line solution, you can increase the no. of HW accelerators if L1 processing increased, and you can increase the no. of COTS CPUs in case of L2 or L3 processing increase, unlike look-aside solution which requires to increase the no. of COTS CPUs if any of L1, L2 or L3 processing increased as COTS CPU is handling all of them. Also, from capacity point of view, if we have huge traffic, then look-aside solution can be an issue as the data of the L1 selected functions will be sent back-and-forth to the hardware accelerator which will affect the processing time and hence can affect the latency-sensitive services, while in-line solution will be a better option. From energy efficiency, look-aside solution is more energy efficient at low-capacity sites, while in-line is more energy efficient at high-capacity sites.
- Me: This is a very difficult question to answer
-
My friend: So, which approach can be used in mobile networks?
- Me: I think it should be a mix of both approaches as simply each mobile network is having a mix of different solutions such as low-capacity sites, high-capacity sites, Centralized RAN, Distributed RAN, etc. So, you can use look-aside approach at low-capacity sites as it is more energy efficient, while you can use in-line approach for Centralized RAN sites as it is more energy efficient at sites with high traffic and also offers better delay than the 5G Fronthaul requirements.
-
My friend: Thank you very much, you made it very clear.
- Me: You are welcome.
LinkedIn: ![]()