-
The g-NB controls the EPS Fallback triggering mechanism to be followed by the UE.
-
EPS Fallback supports two types of triggering methods: Handover or RRC Release with redirection (RWR). Both can be based on measurement or blind-based, but the handover part is usually used with measurements. It’s not recommended to use a blind handover procedure without measurements.
Now, lets go through the details of EPS Fallback triggering mechanisms.
- RRC Release with Redirection EPS Fallback (Blind & Measurement)
-
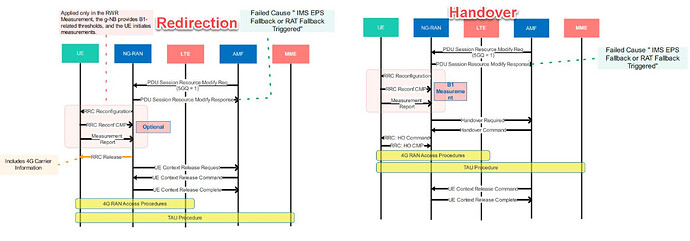
As shown in the below Signaling call flow, An RRC Release with Redirection uses the RRC Release message to specify a target carrier. This procedure does not specify a target cell.
-
In the case of Blind Release with redirection, the g-NB will guide the UE to the 4G network, specifying a designated LTE frequency. If multiple frequencies are defined, the g-NB will choose the frequency based on the defined voice priority, delivering the one with the highest priority to the UE.
-
In the case of Measurement Release with redirection, the g-NB initially sends the RRC Reconfiguration message, incorporating B1-related events, to the UE. Subsequently, the UE commences measuring the reported 4G frequencies in the RRC Reconfiguration message, reporting the measurements to the g-NB through a Measurement Report. The g-NB then will redirect the UE to the reported LTE Frequency.
- Measurement Based IRAT Handover EPS Fallback
- A handover uses the RRC Reconfiguration message to specify a target cell. Handover procedures usually take advantage of measurements to identify the target cell but it is also possible to use a blind handover procedure without measurements
What are the advantages and disadvantages of these triggering methods?
Blind RWR:
-
Pros:
- It features simplified planning as it only necessitates the definition of the 4G frequency.
- It provides a shorter EPS call setup time delay, approximately 200~500 msec, compared to measurement-based methods, though this duration may vary across different networks.
-
Cons:
- High PS Interruption
- Less Success Rate
- E2E Success Rate can`t be measured from OSS KPIs
Measurement RWR:
-
Pros:
- It features simplified planning as it only necessitates the definition of the 4G frequency.
- High Success Rate
-
Cons:
- High PS Interruption
- E2E Success Rate can`t be measured from OSS KPIs
Measurement Handover:
-
Pros:
- High Success Rate
- E2E Success Rate can be evaluated from the OSS KPIs
- less PS Interruption
-
Cons:
- Complicated planning (Relation definition, TAC, etc.)
- High Call Setup Time delay
LinkedIn: ![]()