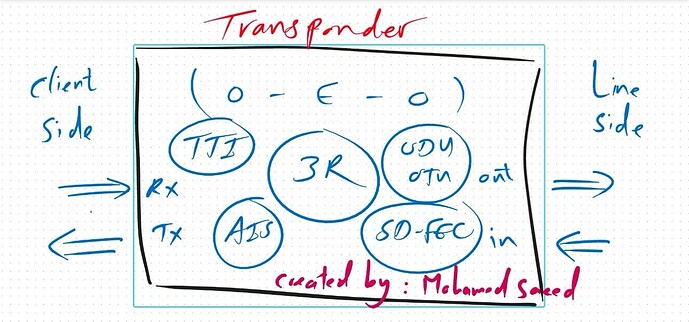
A transponder is a crucial component in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) networks, serving multiple functions in signal processing and transmission.
Key Functions of a Transponder:
- Client-Side Interface:
- Acts as an intermediary between client devices and the DWDM infrastructure.
- Receives client traffic and converts it from an optical signal to an electrical signal for processing.
- Converts the processed signal back into an optical format for transmission.
- Layer 1 (L1) Processing:
- Electrical-layer signal processing (L1) is performed within the transponder.
- This includes signal conditioning before retransmission.
- Port Configuration:
- Client-Side Ports: Connect to external client devices.
- Line-Side Ports: Connect to an optical multiplexer node and follow DWDM spectral compliance (C-band or related spectrum).
- Signal Regeneration (3R Process):
- When used as a repeater, a transponder improves signal quality for long-distance transmission through 3R processing:
- Re-synchronization
- Re-shaping
- Re-amplification
- OTN Overhead Processing:
- Trail Trace Identifier (TTI): A field in the Optical Transport Network (OTN) frame used to identify the source node or circuit.
- Soft Decision Forward Error Correction (SD-FEC): Error detection and correction for enhanced data reliability.
- ODU & OTU Layers: The transponder processes Optical Data Unit (ODU) and Optical Transport Unit (OTU) frames.
- Multiplexing with a Muxponder:
- A muxponder combines multiple lower-rate client signals into a single, higher-capacity frame for efficient DWDM channel utilization.
- In-Band Management:
- Uses General Communication Channel (GCC) bytes for internal network management.
- Fault Indication & Alarm Handling:
- Alarm Indication Signal (AIS): Signals a client-side failure to the remote end.
- Optical-Electrical-Optical (OEO) Conversion:
- Converts a gray (non-DWDM) optical signal to an electrical signal and then back to a colored DWDM optical signal for transmission.
This comprehensive role makes the transponder essential in ensuring seamless, high-quality, and long-distance optical communication within DWDM networks.
LinkedIn: ![]()