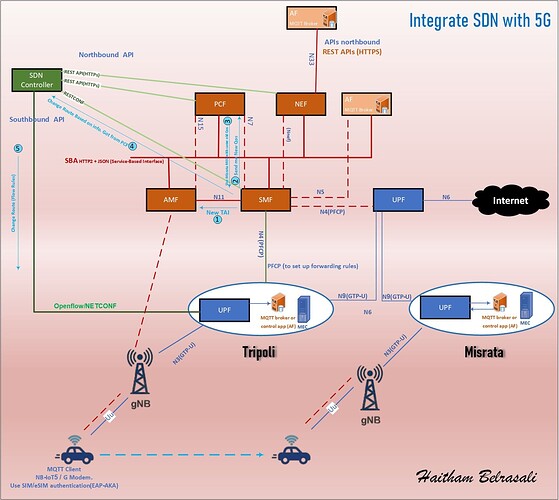
The 5G Core network is built on the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) concept,
while SDN (Software Defined Networking) is based on the separation of the Control Plane and Data Plane.
![]() Therefore, the interaction between them happens only at the Control Plane level.
Therefore, the interaction between them happens only at the Control Plane level.
That means the SDN Controller does not directly connect to the SBA interfaces — instead, it manages the data path through APIs.
![]() SDN Controller ↔ SMF Interface
SDN Controller ↔ SMF Interface
![]() Purpose:
Purpose:
• Enable the SMF to select or create the proper data path through SDN (e.g., create GTP-U paths between gNB and UPF).
• Used during UE relocation to another UPF.
• Update QoS policies dynamically.
![]() SDN Controller ↔ PCF Interface
SDN Controller ↔ PCF Interface
![]() Purpose:
Purpose:
• Retrieve QoS policies from the PCF and apply them on the actual network level.
![]() Example:
Example:
The PCF sends: Delay ≤ 10 ms , Bandwidth ≥ 5 Mbps
![]()
The SDN Controller translates these policies into Flow Rules (routing or priority rules).
![]()
Then it sends them to the UPF via the OpenFlow interface.
![]() SDN Controller ↔ NEF / AF Interface
SDN Controller ↔ NEF / AF Interface
![]() Purpose:
Purpose:
• Allow applications (AF) to request custom paths or QoS levels.
• The SDN Controller provides the optimal path with the lowest delay between the car and the MEC broker.
![]()
![]() This is crucial in Car IoT and MEC scenarios.
This is crucial in Car IoT and MEC scenarios.
Because the application must control the path based on location or real-time conditions.
![]() SDN Controller ↔ UPF Interface
SDN Controller ↔ UPF Interface
![]() Purpose:
Purpose:
• Program or modify Flow Rules inside the UPF.
• Apply SMF policies directly in the Data Plane.
Practical Example: Car Handover from Tripoli to Misurata ![]()
![]() The car moves from Tripoli MEC to Misurata MEC.
The car moves from Tripoli MEC to Misurata MEC.
![]() The SMF reports the new location (TAI) to the AMF.
The SMF reports the new location (TAI) to the AMF.
![]() The SMF requests new area policies (QoS) from the PCF.
The SMF requests new area policies (QoS) from the PCF.
![]() The PCF replies: “Use UPF-Misurata + keep the same QoS.”
The PCF replies: “Use UPF-Misurata + keep the same QoS.”
![]() The SMF instructs the SDN Controller to update the data path.
The SMF instructs the SDN Controller to update the data path.
![]() The SDN Controller sends new Flow Rules to the UPF via OpenFlow.
The SDN Controller sends new Flow Rules to the UPF via OpenFlow.
![]() The AF transfers the MQTT session to maintain the connection at the application layer.
The AF transfers the MQTT session to maintain the connection at the application layer.
![]() The NEF notifies the AF that the session will move to the new MQTT Broker in Misurata.
The NEF notifies the AF that the session will move to the new MQTT Broker in Misurata.
![]() The AF connects to the new broker — session migration happens smoothly.
The AF connects to the new broker — session migration happens smoothly.
![]() Result:
Result:
The MQTT session continues without any noticeable interruption to the user. ![]()
![]() Summary:
Summary:
![]() SDN links network policies (SMF/PCF) with applications (AF/NEF) and data paths (UPF).
SDN links network policies (SMF/PCF) with applications (AF/NEF) and data paths (UPF).
![]() Ensures dynamic flexibility and service continuity, especially in MEC and Car IoT scenarios.
Ensures dynamic flexibility and service continuity, especially in MEC and Car IoT scenarios.
![]() SMF maintains the session at the network level.
SMF maintains the session at the network level.
![]() AF (MQTT Broker) maintains the session at the application level.
AF (MQTT Broker) maintains the session at the application level.
LinkedIn: ![]()