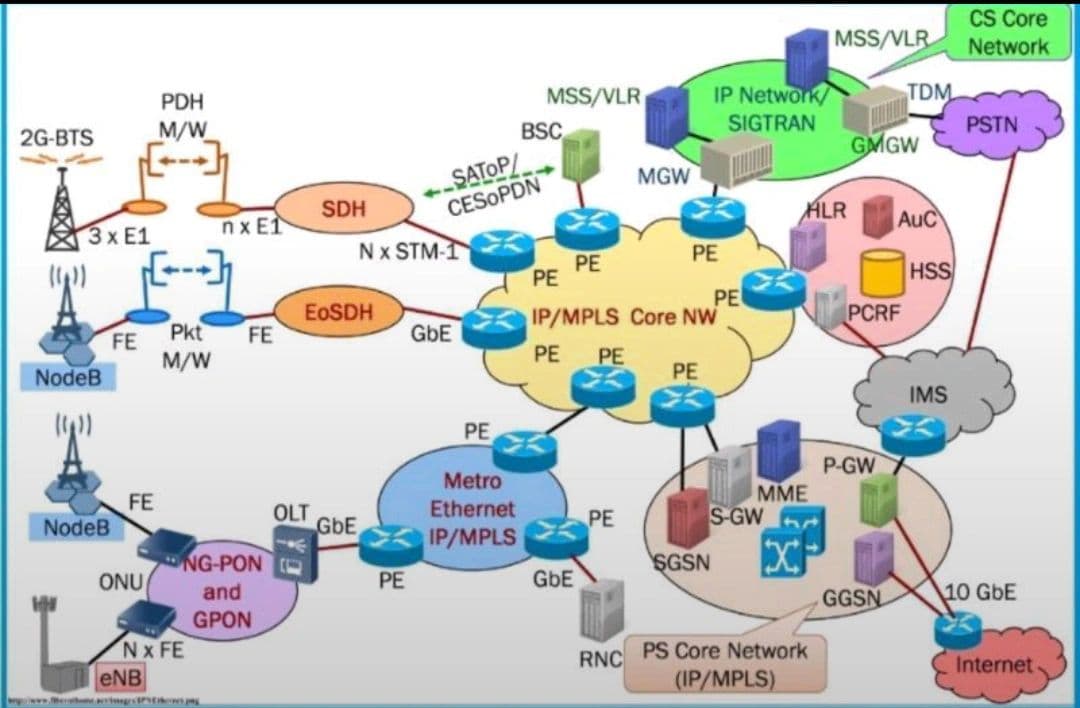
This diagram represents a telecommunication network architecture that integrates 2G, 3G, and 4G (LTE) mobile technologies and their connections to the core network and the Internet. It outlines how data flows from the radio access network to the core network and external networks. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Radio Access Networks (RAN)
These are the networks that directly connect user devices to the network.
2G (GSM)
2G-BTS (Base Transceiver Station) connects via 3xE1 lines to the PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy) network.
Then connects to SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) via multiple E1s.
SDH connects to the IP/MPLS Core Network using STM-1 and protocols like SAToP/CEoP/PDN.
3G (UMTS)
NodeB connects through FE (Fast Ethernet) and Packet Microwave to EoSDH (Ethernet over SDH).
EoSDH then connects via Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) to IP/MPLS Core Network.
4G (LTE)
eNodeB connects to ONU (Optical Network Unit) using multiple FE connections.
ONU is part of GPON/NG-PON architecture.
Then goes to OLT (Optical Line Terminal), which outputs via GbE to Metro Ethernet IP/MPLS.
This connects to the IP/MPLS Core Network.
2. Aggregation and Transport Networks
Metro Ethernet and EoSDH aggregate traffic from various RAN technologies and feed into the IP/MPLS Core Network.
IP/MPLS Core Network is the central transport layer (cloud in the center) with multiple PE (Provider Edge) routers.
3. Core Networks
Circuit-Switched Core (CS Core Network - Green Section)
Connected to MGW (Media Gateway) and MSS/VLR (Mobile Switching Center / Visitor Location Register).
These interact with PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) for voice services.
Uses SIGTRAN over IP Network for signaling.
Packet-Switched Core (PS Core Network - Orange Section)
Includes:
MME (Mobility Management Entity)
S-GW (Serving Gateway)
P-GW (Packet Gateway)
SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node)
GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node)
These elements manage mobility and data sessions for 3G/4G users.
4. Other Core Functions
HLR (Home Location Register), HSS (Home Subscriber Server), AuC (Authentication Center), and PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function) handle user authentication, session rules, and charging.
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) is used for IP-based voice/video services (VoLTE, VoWiFi).
5. External Network
Internet is reached via 10 GbE links from the P-GW.
Core components route and secure traffic to and from the external world.
This architecture represents how telecom operators integrate legacy (2G/3G) and modern (4G) networks into a single IP/MPLS-based transport and core infrastructure, enabling efficient data, voice, and control traffic management. Let me know if you’d like a more focused explanation of a specific part (e.g., LTE flow, or CS Core).
LinkedIn: ![]()