In the pictures below, you can find an explanation of the main functions of each layer, along with a detailed explanation of SDAP
SDAP Protocol: Simple Brief
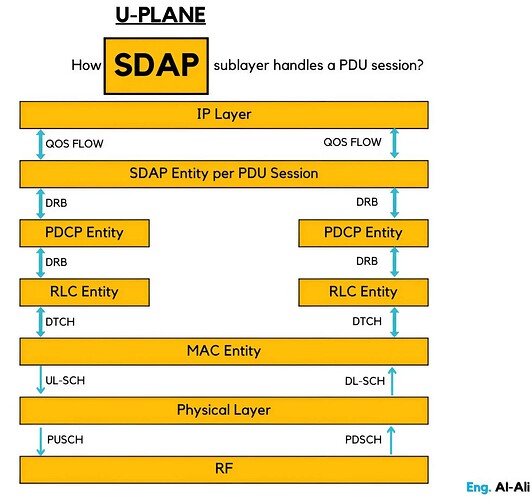
SDAP sublayer exists only in the user plane in both gNB and UE. It interfaces to upper layers via QoS flows and to the PDCP lower layer via Data Radio Bearers (DRBs). Traffic from QoS flows are mapped to suitable DRBs. This is an essential role of SDAP. SDAP layer doesn’t exist in 4G/LTE since QoS flows were introduced only in 5G.
Main Functions of SDAP
-
QoS Flow Mapping: SDAP maps multiple QoS flows to Data Radio Bearers (DRBs). This mapping allows for differentiation between user data types, assigning higher priority to certain types of traffic (e.g., video calls vs. web browsing).
-
Reflective QoS: This feature enables the UE to observe downlink QoS flow-to-DRB mappings and apply the same rules to uplink traffic. It simplifies configuration by allowing the UE to “reflect” downlink behavior in the uplink.
-
SDAP Header: SDAP PDUs (Protocol Data Units) may include a 1-byte header that contains QoS flow ID (QFI) and flags for Reflective QoS. The header is optional when the DRB handles only a single QoS flow, but it’s necessary for managing multiple flows.
-
End-Marker Control PDU: SDAP includes an end-marker control PDU to signal the end of a QoS flow mapping on a DRB. This ensures that traffic no longer gets routed to a specific DRB once the mapping is removed.
SDAP in PDU Sessions
In 5G, a PDU session is like a data connection that you use for internet or other online services. Each session can handle different types of data, like a video call, a download, or gaming traffic. These different types of data are grouped into QoS flows - streams of data that have different levels of priority based on their importance.
For example:
- Video call needs high priority to avoid delay.
- Downloading may take some time.
The SDAP layer takes these QoS flows and decides how to map them to Data Radio Bearers (DRBs), which are like the communication channels between your phone and the network. Each DRB can handle one or more QoS flows, depending on the data needs.
So, SDAP’s job is to make sure that each QoS flow is sent over the right DRB, ensuring the most important data (like video calls) gets priority over less urgent traffic (like background downloads).
SDAP was introduced in 5G to manage the new QoS flows that 5G relies on to handle different types of data traffic. Unlike 4G, where data handling was less flexible
Note: The SDAP is only present in Standalone (SA) 5G networks. In Non-Standalone (NSA) networks, the SDAP protocol is not used.
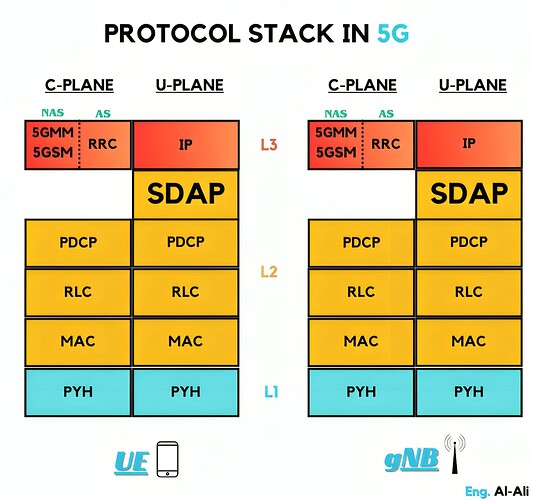
Protocol Stack in 5G
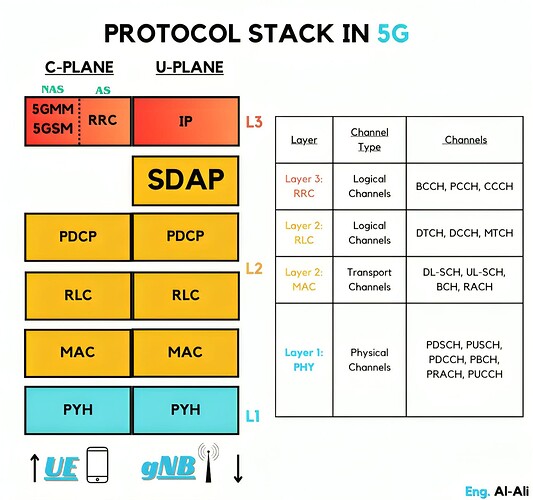
Protocol Stack in 5G (cont.)
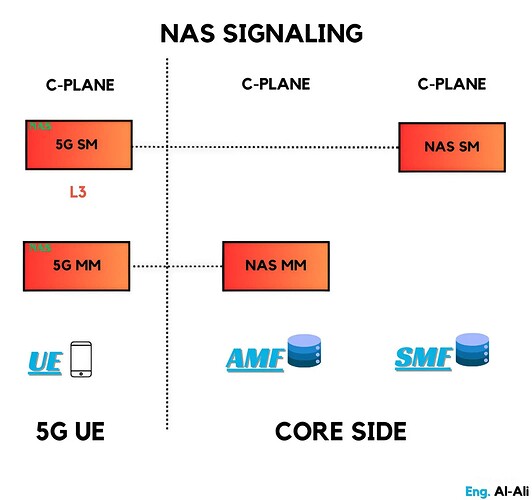
NAS Signaling
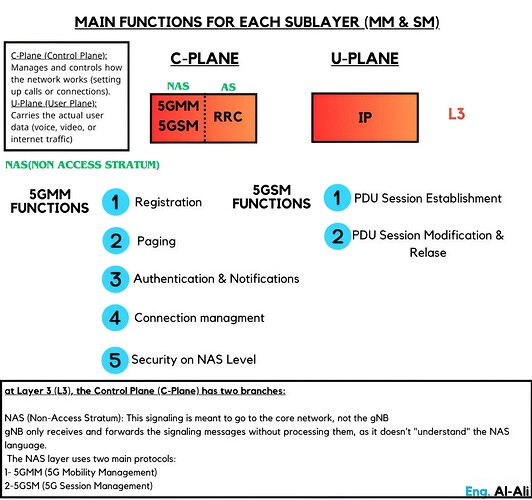
Main functions for each sublayer (MM & SM)
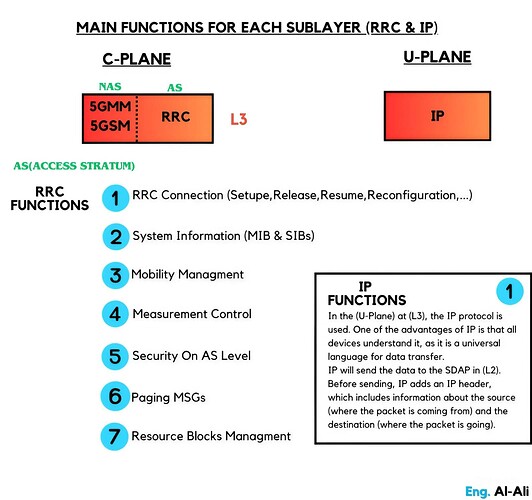
Main functions for each sublayer (RRC & IP)
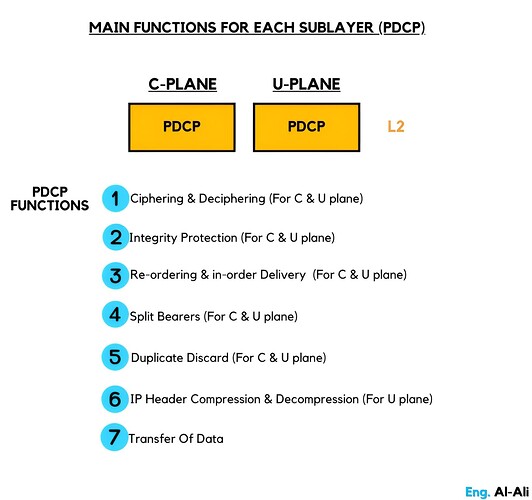
Main functions for each sublayer (PDCP)
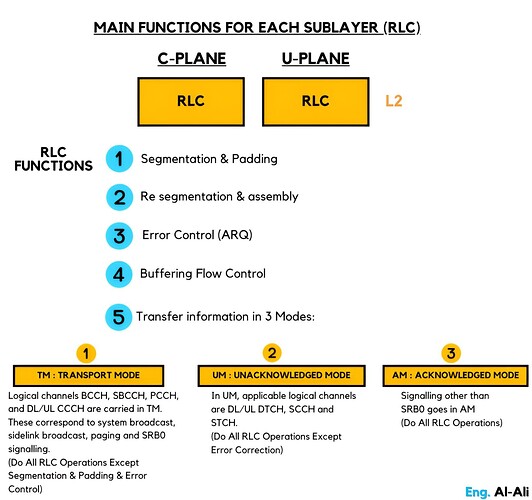
Main functions for each sublayer (RLC)
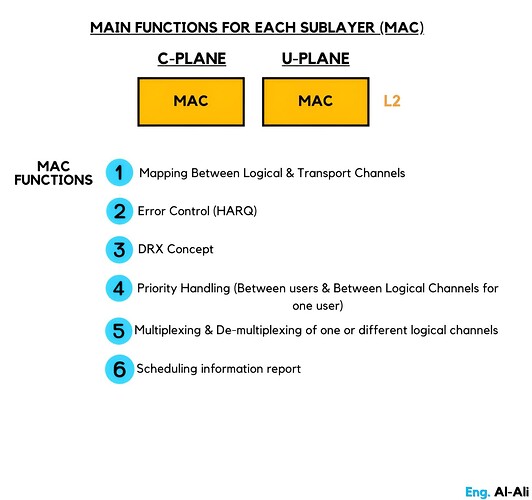
Main functions for each sublayer (MAC)
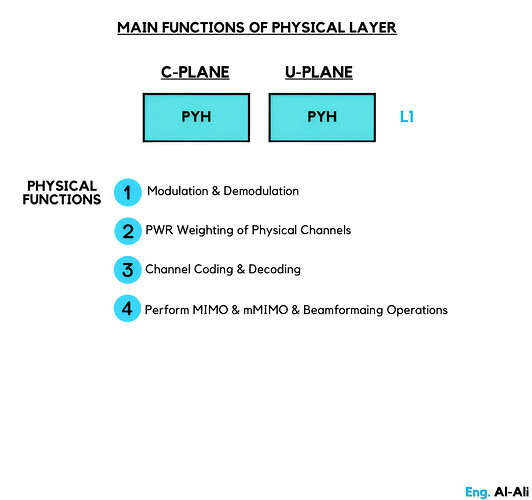
Main functions of Physical Layer
How SDAP sublayer handles a PDU session
LinkedIn: ![]()