![]() Private 5G Networks: Architecture Variations & Choosing the Right One for Your Use Case
Private 5G Networks: Architecture Variations & Choosing the Right One for Your Use Case ![]()
As the world evolves with the advent of Private 5G networks, it’s crucial to understand the different architecture variations and the importance of selecting the correct one per your use case to achieve optimal results. ![]()
There are three main architecture variations in Private 5G networks as per Nokia’s Vision:
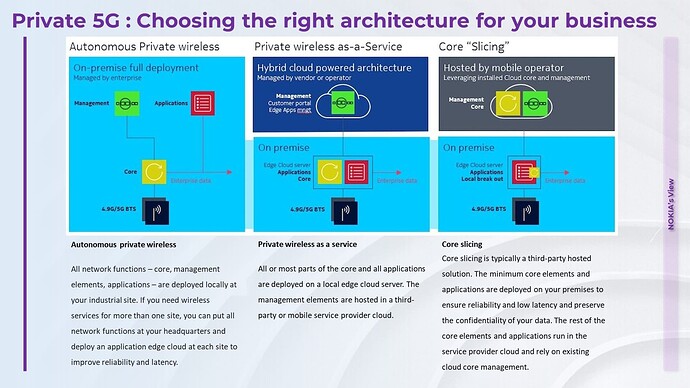
![]() Autonomous private wireless - All network functions – core, management elements, applications – are deployed locally at your industrial site. However, based on your need for wireless services for multiple sites, you can put all network functions at your headquarters and deploy an application edge cloud at each location to improve reliability and latency.
Autonomous private wireless - All network functions – core, management elements, applications – are deployed locally at your industrial site. However, based on your need for wireless services for multiple sites, you can put all network functions at your headquarters and deploy an application edge cloud at each location to improve reliability and latency.
![]() Private wireless as a service - All or most parts of the core and all applications are deployed on a local edge cloud server. The management elements are hosted in a third-party or mobile service provider cloud.
Private wireless as a service - All or most parts of the core and all applications are deployed on a local edge cloud server. The management elements are hosted in a third-party or mobile service provider cloud.
![]() Core slicing - Core slicing is typically a third-party hosted solution. The minimum core elements and applications are deployed on your premises to ensure reliability and low latency and preserve the confidentiality of your data. The rest of the core elements and applications run in the service provider’s cloud and rely on existing core management.
Core slicing - Core slicing is typically a third-party hosted solution. The minimum core elements and applications are deployed on your premises to ensure reliability and low latency and preserve the confidentiality of your data. The rest of the core elements and applications run in the service provider’s cloud and rely on existing core management.
Selecting the right architecture depends on factors like the need for roaming, security requirements, and cost considerations. For example, a Localised Core architecture may be the best choice if your use case demands high security and performance.
Moreover, implementing UPF (User Plane Function) in your Private 5G network can help you better manage data traffic and improve overall network performance.
To sum up, understanding the different Private 5G architecture variations is essential to make an informed decision and ensuring your use case’s success. So, choose wisely and unlock the full potential of Private 5G networks! ![]()
![]()
LinkedIn: ![]()