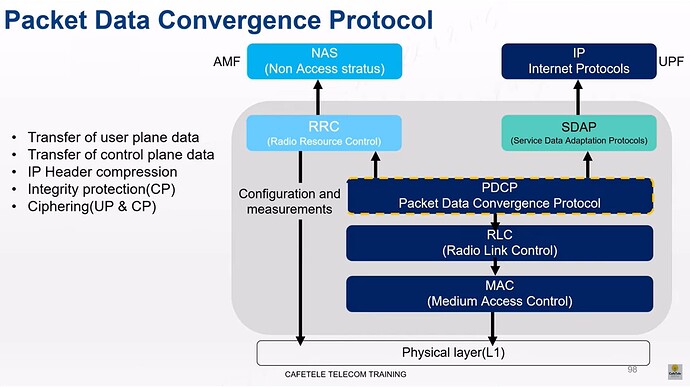
The Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) in 5G New Radio (NR) plays a crucial role in the air interface protocol stack, interfacing between the Radio Link Control (RLC) layer and the upper layers of the network, such as the IP layer. PDCP performs several key functions to ensure efficient and secure data transmission over the air interface in 5G networks. Here are the main functions and features of PDCP in 5G NR:
-
Header Compression and Decompression: To efficiently use the radio interface bandwidth, PDCP applies header compression and decompression mechanisms, such as Robust Header Compression (RoHC). This reduces the size of IP headers, which is particularly beneficial for small IP packets, as it significantly reduces the overhead.
-
Encryption and Decryption: PDCP is responsible for encrypting and decrypting user data to ensure the confidentiality of information transmitted over the air. This is critical for maintaining user privacy and security in 5G networks.
-
Integrity Protection and Verification: For control plane data, PDCP provides integrity protection and verification to ensure that the data has not been tampered with during transmission. This is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of signaling messages.
-
Sequence Numbering: PDCP assigns sequence numbers to packets to support in-order delivery and to detect any missing packets. This is important for reordering packets that arrive out of order and for detecting and possibly retransmitting lost packets.
-
Duplicate Elimination: Due to the retransmission mechanisms at lower layers (e.g., RLC), PDCP may receive duplicate packets. It is responsible for eliminating these duplicates to ensure that upper layers receive each packet only once.
-
User Plane and Control Plane Services: PDCP serves user plane data (e.g., internet traffic) and control plane data (e.g., signaling messages). It applies different processing rules depending on the data type, such as integrity protection only for control plane data.
-
SDAP Integration: In 5G NR, a new layer called the Service Data Adaptation Protocol (SDAP) has been introduced above PDCP for QoS flow management in the user plane. PDCP interacts with SDAP to ensure that QoS requirements for different services are met.
-
Support for Split Architecture: PDCP supports flexible deployment architectures, such as splitting the gNB functionality into a centralized unit (CU) and a distributed unit (DU). This allows for the relocation of PDCP functionality between the CU and DU based on the deployment needs.
Watch Video on Youtube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G3iQ7am1-b4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G3iQ7am1-b4
LinkedIn: ![]()