The 5G Core Network is built on a diverse set of protocols that enable seamless communication and advanced capabilities. Let’s break it down into structured categories:
-
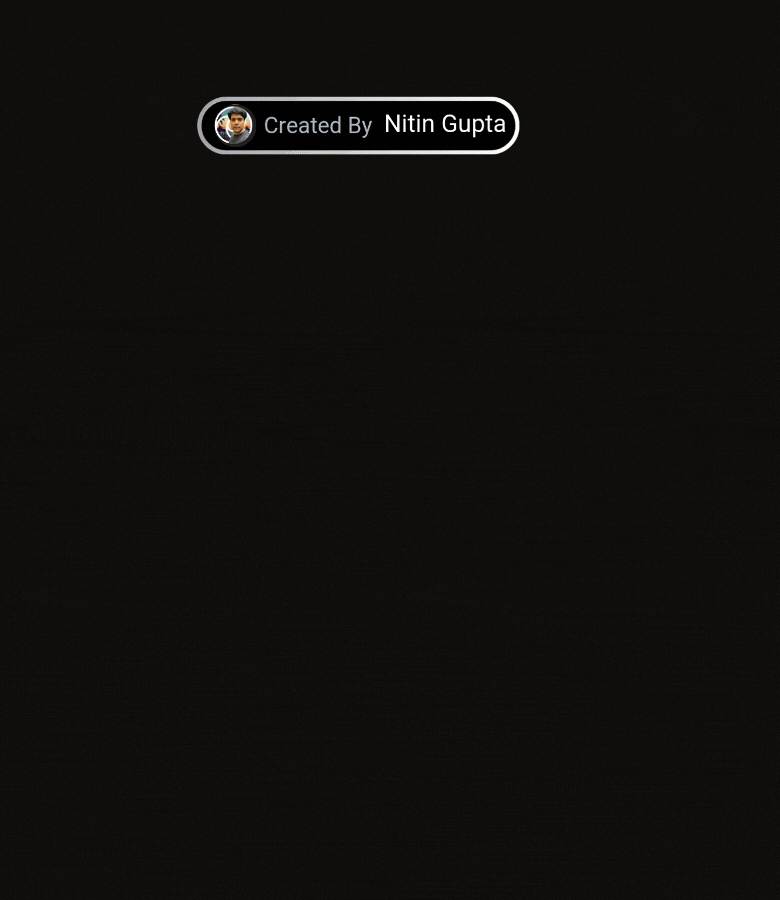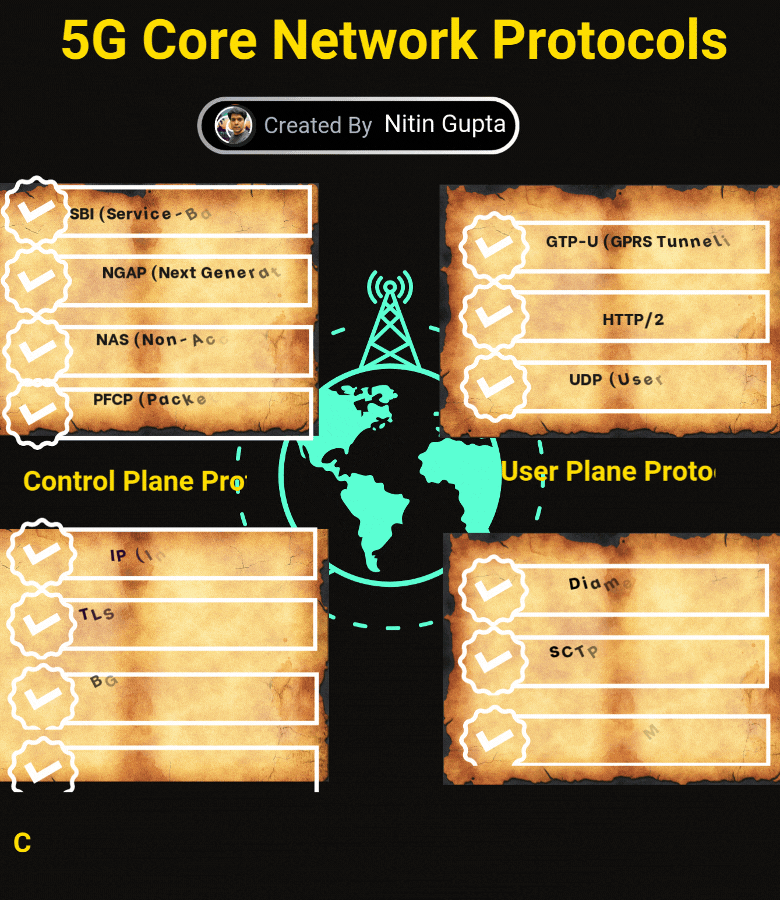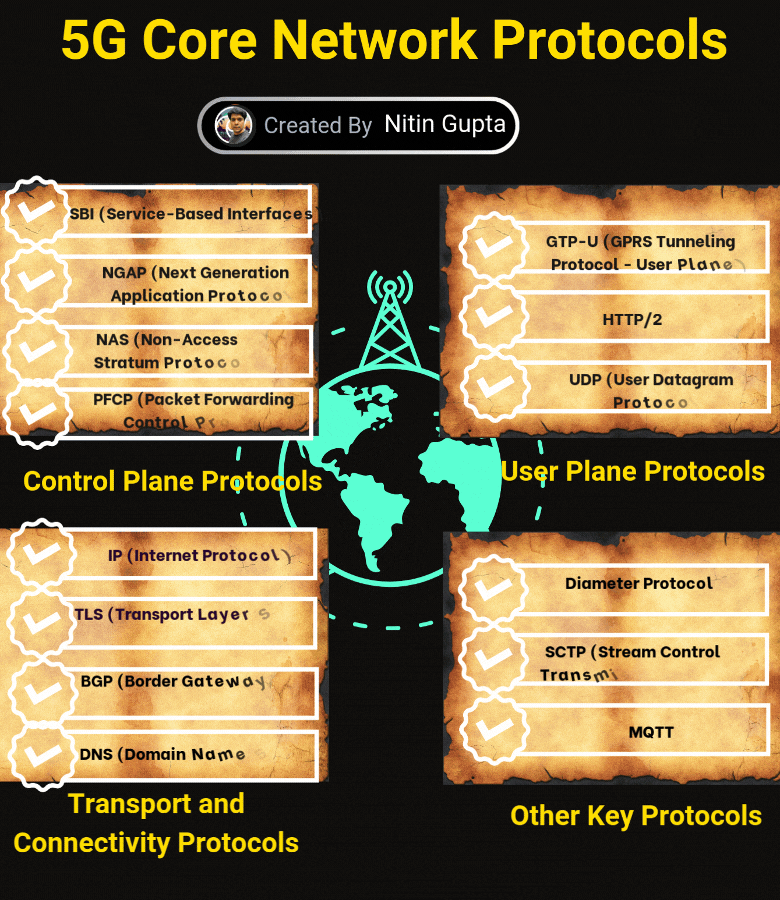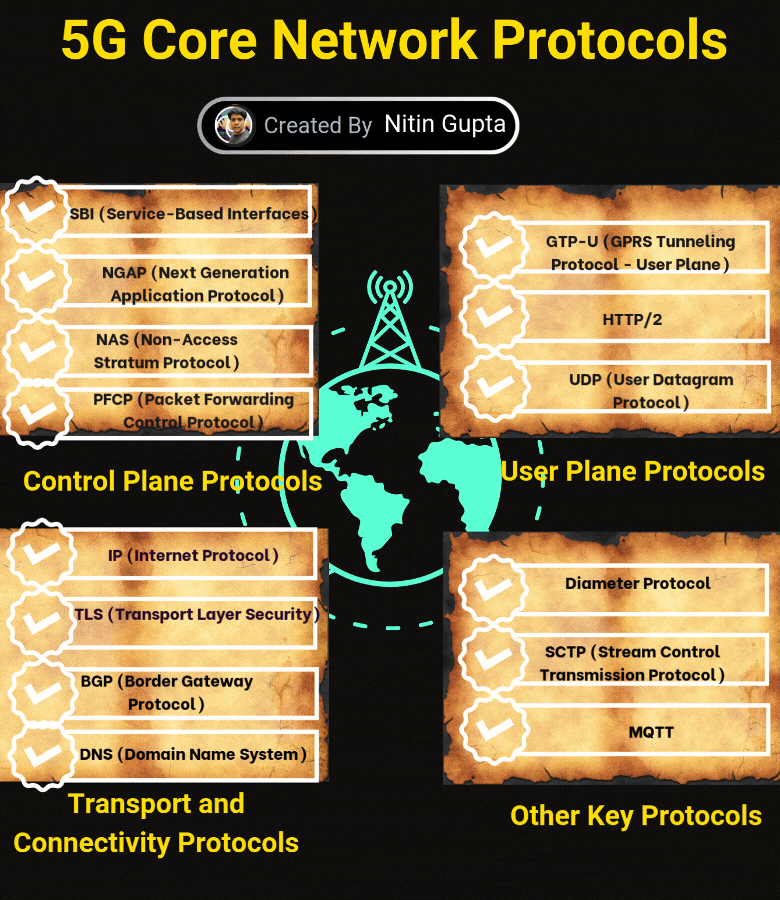
Control Plane Protocols
-
SBI (Service-Based Interfaces): Supports service-based communication between network functions.
-
NGAP (Next Generation Application Protocol): Manages signaling between the gNB and the core network.
-
NAS (Non-Access Stratum Protocol): Handles control messages between the user device and core.
-
PFCP (Packet Forwarding Control Protocol): Enables control of user plane functions and sessions.
-
-
User Plane Protocols
-
GTP-U (GPRS Tunneling Protocol – User Plane): Ensures efficient data transfer.
-
HTTP/2: Optimized communication for service-based architecture.
-
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Ensures low-latency data transmission.
-
-
Transport and Connectivity Protocols
-
IP (Internet Protocol): Core protocol for routing data.
-
TLS (Transport Layer Security): Secures data communication.
-
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): Manages routing between different networks.
-
DNS (Domain Name System): Resolves domain names to IP addresses.
-
-
Other Key Protocols
-
Diameter Protocol: Handles authentication, authorization, and accounting.
-
SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol): Ensures reliable signaling transmission.
-
MQTT: Lightweight messaging protocol for IoT devices.
-
- Why These Protocols Matter:
Each protocol plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability, scalability, and security of 5G networks. From managing control signals to enabling ultra-fast data transfer, these protocols are the backbone of 5G connectivity.
LinkedIn: ![]()