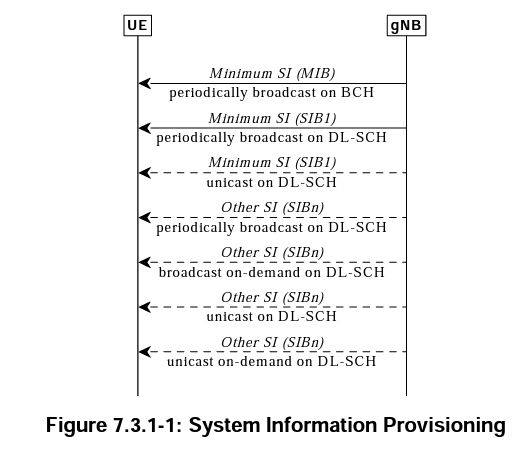
The Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) is a fundamental downlink-only logical channel in LTE networks. Its primary function is to broadcast essential System Information (SI) from the eNodeB to all User Equipment (UEs) within a cell, enabling them to synchronize, identify the network, and prepare for access.
![]() BCCH delivers SI via two main message types:
BCCH delivers SI via two main message types:
![]() Master Information Block (MIB): Contains the most critical, time-sensitive parameters needed for initial synchronization and decoding further system information. Key MIB contents (typically 24 bits) include:
Master Information Block (MIB): Contains the most critical, time-sensitive parameters needed for initial synchronization and decoding further system information. Key MIB contents (typically 24 bits) include:
![]() Downlink System Bandwidth (e.g., 1.4 to 20 MHz).
Downlink System Bandwidth (e.g., 1.4 to 20 MHz).
![]() PHICH (Physical HARQ Indicator Channel) Configuration.
PHICH (Physical HARQ Indicator Channel) Configuration.
![]() System Frame Number (SFN - most significant bits).
System Frame Number (SFN - most significant bits).
![]() Antenna Configuration (often inferred via CRC masking during decoding).
Antenna Configuration (often inferred via CRC masking during decoding).
![]() MIB Transmission
MIB Transmission ![]()
![]() Mapping: BCCH (MIB)
Mapping: BCCH (MIB) ![]() BCH (Broadcast Channel - Transport)
BCH (Broadcast Channel - Transport) ![]() PBCH (Physical Broadcast Channel)
PBCH (Physical Broadcast Channel)
![]() Physical Channel: The PBCH is robustly transmitted using QPSK modulation in the central 72 subcarriers (6 Resource Blocks) of the downlink bandwidth, regardless of the total system bandwidth. This fixed location allows UEs to find it without prior knowledge of the cell’s bandwidth.
Physical Channel: The PBCH is robustly transmitted using QPSK modulation in the central 72 subcarriers (6 Resource Blocks) of the downlink bandwidth, regardless of the total system bandwidth. This fixed location allows UEs to find it without prior knowledge of the cell’s bandwidth.
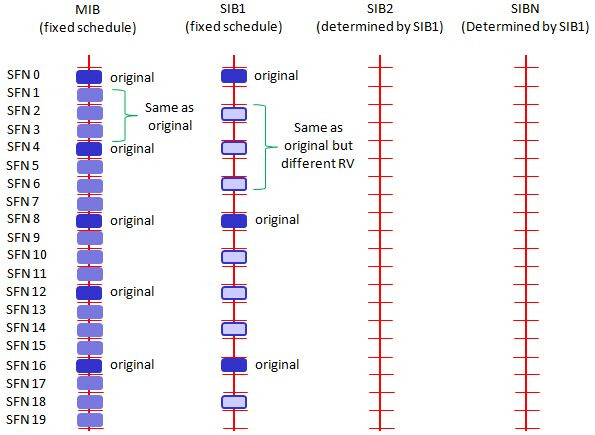
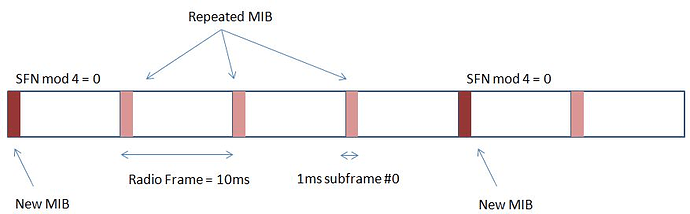
![]() Timing: The MIB content updates every 40ms, but the PBCH carrying it is transmitted every 10ms (in subframe 0 of each radio frame), allowing for repetition and reliable decoding even at cell edges.
Timing: The MIB content updates every 40ms, but the PBCH carrying it is transmitted every 10ms (in subframe 0 of each radio frame), allowing for repetition and reliable decoding even at cell edges.
![]() System Information Blocks (SIBs): Provide more detailed configuration parameters.
System Information Blocks (SIBs): Provide more detailed configuration parameters.
![]() SIB1: Cell access information (PLMN ID, Tracking Area Code, Cell ID, Cell Barring status), and crucial scheduling details (periodicity, window) for other SIBs.
SIB1: Cell access information (PLMN ID, Tracking Area Code, Cell ID, Cell Barring status), and crucial scheduling details (periodicity, window) for other SIBs.
![]() SIB2: Common channel configurations, including Random Access Channel (RACH) parameters and radio resource configurations.
SIB2: Common channel configurations, including Random Access Channel (RACH) parameters and radio resource configurations.
![]() Other SIBs (SIB3-SIB8+): Cell reselection parameters, neighbor cell information, etc.
Other SIBs (SIB3-SIB8+): Cell reselection parameters, neighbor cell information, etc.
![]() SIB Transmission
SIB Transmission ![]()
![]() Mapping: BCCH (SIBs)
Mapping: BCCH (SIBs) ![]() DL-SCH (Downlink Shared Channel - Transport)
DL-SCH (Downlink Shared Channel - Transport) ![]() PDSCH (Physical Downlink Shared Channel)
PDSCH (Physical Downlink Shared Channel)
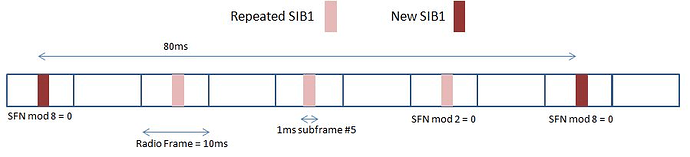
![]() Scheduling: SIB1 has a fixed periodicity of 80ms and specific transmission opportunities (e.g., in subframe #5 when SFN mod 8 = 0, repeated when SFN mod 2 = 0). Its exact location on the PDSCH is dynamically scheduled and indicated via the PDCCH (using SI-RNTI).
Scheduling: SIB1 has a fixed periodicity of 80ms and specific transmission opportunities (e.g., in subframe #5 when SFN mod 8 = 0, repeated when SFN mod 2 = 0). Its exact location on the PDSCH is dynamically scheduled and indicated via the PDCCH (using SI-RNTI).
![]() Other SIBs: Scheduled according to the information provided in SIB1, also carried on the PDSCH. Typical periodicities might be 160ms for SIB2, 320ms+ for others, but this is configurable.
Other SIBs: Scheduled according to the information provided in SIB1, also carried on the PDSCH. Typical periodicities might be 160ms for SIB2, 320ms+ for others, but this is configurable.
![]() Critical Importance
Critical Importance
A UE must successfully decode the MIB (via PBCH) first. Using information from the MIB (like bandwidth and SFN timing), it can then locate and decode SIB1 (on PDSCH). Only after decoding SIB1 does the UE have enough information (network identity, access parameters, RACH configuration from SIB2 whose schedule is in SIB1) to attempt network access. Failure to decode MIB or SIB1 leaves the UE unable to camp on or connect to the cell.
LinkedIn: ![]()