-
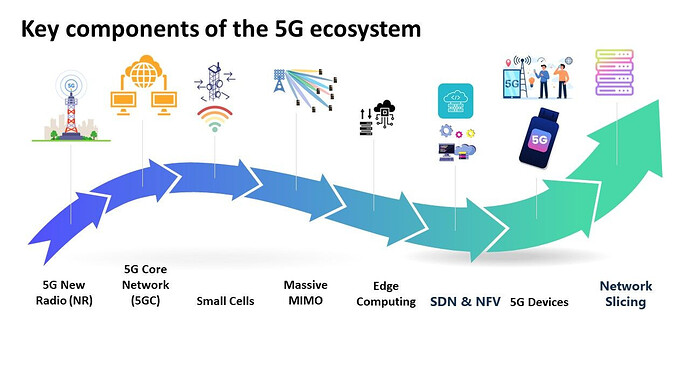
5G New Radio (NR): This is the global standard for a unified, more capable 5G wireless air interface. It is designed to support a variety of use cases with improved speed, capacity, and functionality compared to previous generations.
-
5G Core Network (5GC): The 5G Core network will allow for greater flexibility and service capabilities compared to the 4G LTE network. It is designed to support network slicing, where different services can have dedicated ‘slices’ of the network with different characteristics.
-
Small Cells: These are mini base stations required for the extensive network coverage and capacity. They are crucial due to the higher frequency bands used in 5G, which have a shorter range.
-
Massive MIMO: Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology uses multiple antennas at the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. Massive MIMO, with a large number of antennas, is an essential component of 5G networks.
-
Edge Computing: This involves processing data closer to where it is generated (at the ‘edge’ of the network), which reduces latency and can be critical for applications that require real-time processing.
-
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV): These technologies allow for more flexible and efficient use of network resources, which is crucial for managing the complexity of 5G networks.
-
5G Devices: These are the end-user devices such as smartphones, IoT devices, and more that are designed to operate with 5G networks. They need to support 5G NR and potentially other technologies such as Wi-Fi 6.
-
Network Slicing: This is a type of network virtualization that allows for the creation of multiple distinct virtual networks with different characteristics on a single physical network. This is critical for supporting the diverse range of use cases and requirements in 5G networks.
-
Network Operators: These are the service providers that operate the 5G networks. They invest in the infrastructure and manage the delivery of services to end-users.
-
Regulatory Bodies: These are organizations like the FCC in the US, or the ITU globally, that regulate the use of radio spectrum and other aspects of telecommunications.
-
Infrastructure Vendors: These are companies like Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia that provide the hardware and software for 5G networks.
-
Chip Manufacturers: Companies like Qualcomm, MediaTek, and others design and manufacture the chips used in 5G devices and infrastructure.
Credits: ![]()