Before we dive deep into Network APIs, let’s first understand what an API is. API stands for Application Programming Interface. It’s a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate with each other. Think of it as a bridge that enables the sharing of data and functionality between different programs, making it easier for developers to create complex applications.
To put it simply, an API defines how different software components should interact, specifying the methods and data formats they should use. This allows developers to build new features and integrate existing services without needing to know the internal workings of the other software.
Google Maps API is one of the most extensively used APIs globally! It provides developers with tools to embed Google Maps on webpages, mobile apps, and other applications, enabling features like displaying maps, searching for locations, and providing directions.
In the digital world, APIs enable applications like social media platforms, payment gateways, and weather services to interact seamlessly, providing users with a richer and more integrated experience.
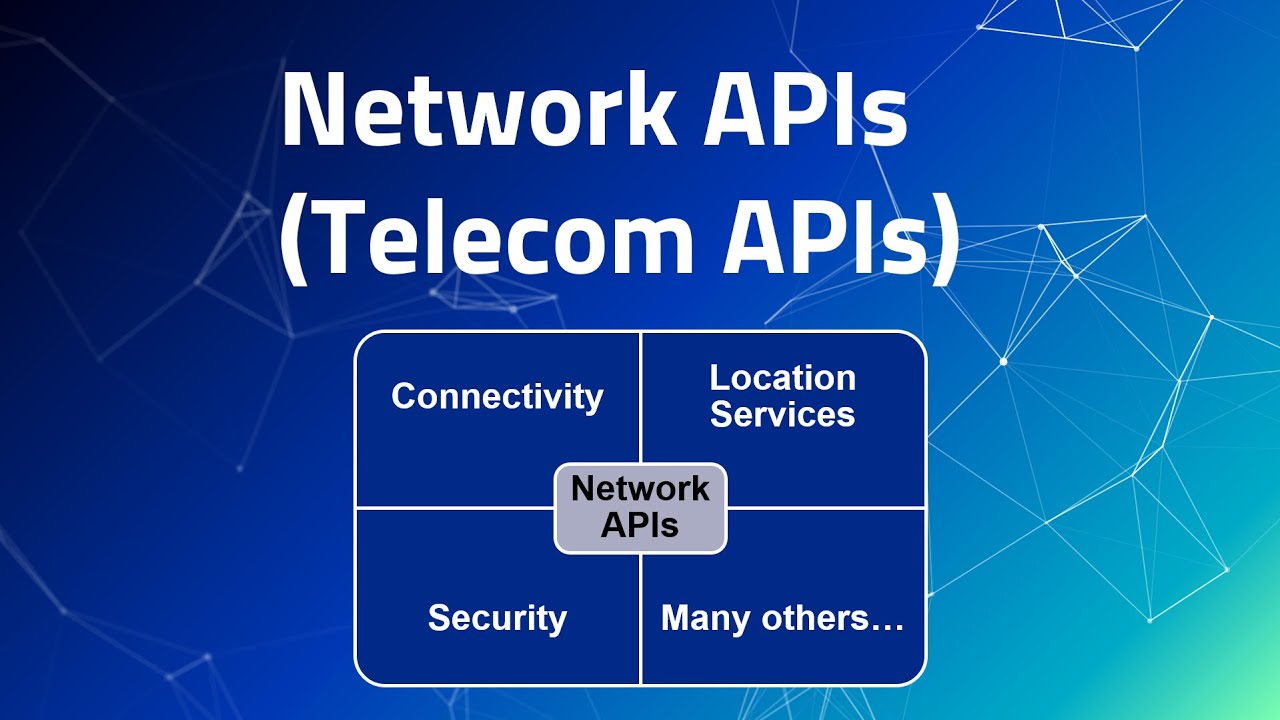
Now, let’s understand Network APIs. A Network API is specifically designed to enable communication and interaction with telecom network capabilities. Network APIs allow developers to access and control network functions and services, such as connectivity, location services, security features, and more.
By using Network APIs, developers can create applications that leverage the advanced features of telecom networks, enabling new and innovative use cases.
Continue to explore: