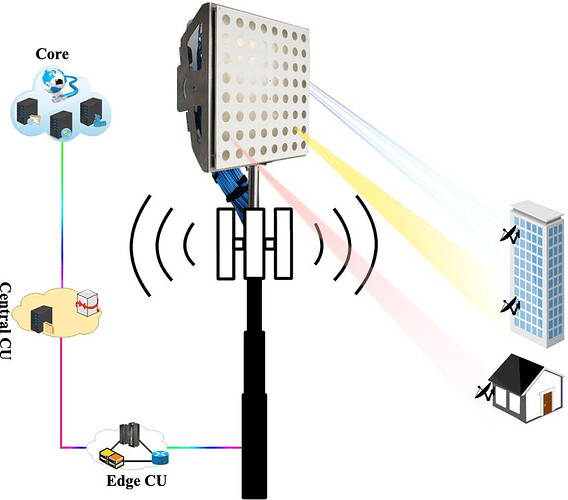
Where to Implement FWA?
- Urban Areas (5G FWA, mmWave) – Fiber & 60GHz backhaul
- Suburban Areas (4G/5G FWA) – Microwave & Fiber Hybrid Backhaul
- Rural Areas (4G FWA) – Microwave, Satellite, & Unlicensed Backhaul
- Remote Areas (LTE/5G FWA) – Satellite or Unlicensed Band Radio Backhaul
- Enterprise Connectivity – Hybrid Microwave & Fiber for SLA-based services
- Temporary Deployments (Disaster recovery, Events, Construction sites) – Unlicensed Band (5 GHz, 60 GHz) & Satellite Backhaul
Backhaul Options for FWA
A. Fiber Optic Backhaul
-
Advantages:
- Highest speed (10–100 Gbps) & ultra-low latency
- Future-proof for high-demand applications
- Reliable & interference-free
-
Disadvantages:
- High deployment cost
- Time-consuming & difficult in remote areas
-
Best for: Dense urban areas, enterprise & mission-critical FWA
B. Microwave Backhaul (Licensed Spectrum)
-
Advantages:
- High capacity (1–10 Gbps)
- Faster deployment than fiber
- Long range (~10-50 km)
-
Disadvantages:
- Expensive spectrum licensing
- Weather-sensitive (Rain fade in high frequencies)
-
Best for: Suburban & rural FWA, areas where fiber is unavailable
C. Unlicensed Band Radio (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 60 GHz, 80 GHz E-band)
-
Advantages:
- No spectrum licensing cost
- Quick & easy deployment
- Cost-effective for small-scale networks
-
Disadvantages:
- Higher interference risk (especially in 5 GHz & 2.4 GHz bands)
- Limited range (especially 60 GHz & 80 GHz)
- Lower reliability than fiber/microwave
-
Best for: Rural broadband, small cell backhaul, and short-range links
D. Satellite Backhaul (LEO/GEO Satellite, Starlink, OneWeb, Viasat)
-
Advantages:
- Covers remote & isolated locations
- Easy deployment, no need for ground infrastructure
-
Disadvantages:
- High latency (especially GEO satellites ~600ms)
- Expensive compared to other options (~$100-500 per Mbps)
- Weather-sensitive
-
Best for: Remote FWA deployments, backup connectivity
Hybrid Backhaul Model for FWA
Combining Multiple Backhaul Types for Maximum Efficiency
-
Urban Areas (High-Density 5G FWA) – Fiber + 60 GHz Backhaul
- Use fiber as primary backhaul for core connectivity
- Deploy 60 GHz unlicensed mmWave for small cells & short-distance backhaul
-
Suburban & Semi-Rural (4G/5G FWA) – Microwave + Fiber Hybrid
- Fiber for main aggregation points
- Licensed microwave (E-band or 5G backhaul) for last-mile connectivity
-
Rural & Low-Density Areas – Microwave + Unlicensed Band Hybrid
- Licensed microwave for main backhaul (~10-30 km)
- Unlicensed 5 GHz/60 GHz for short-distance distribution
-
Remote & Disaster Recovery – Satellite + Unlicensed Radio
- Satellite backhaul for core connectivity
- Local distribution via 5 GHz Wi-Fi / 4G LTE FWA
LinkedIn: ![]()