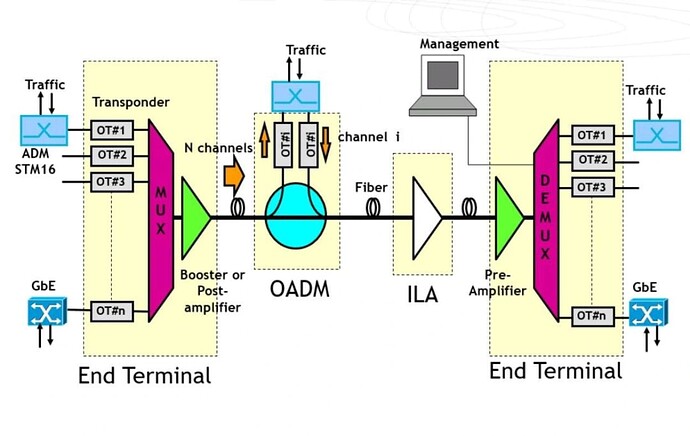
-
OADM is the most important part in the WDM architecture.
-
It’s used for wavelength routing and forwarding.
-
Stands for optical add drop multiplexer.
-
It has 3 types :
- FOADM
Called fixed, it’s used to add and drop fixed predetermined wavelengths.
Configuration is depending on how boards are connected / fibered by site engineer.
This configuration is static and need Manuel intervention to change the configuration.
Advantages: low cost and simplicity.
- ROADM
Called reconfigurable, its used to add wavelengths to the same path, drop specific wavelengths fro the flow in to specific ports , pass through.
It has the capability to dynamically selecting which wavelengths should be dropped or added.
It’s based on WR (wavelength router).
It contain tunable fiber grating modules and circulators to dynamically add / drop.
You can dynamically change its configuration remotely, no need for site visit.
Advantages : flexibily, dynamic, software programmable.
It’s main block called: wavelength selective switch (WSS).
- TOADM
Called tunable , it’s similar to ROADM but its based on whats called CWR.
CWR ( colorless wavelength router ) which give the TOADM the ability to have colorless ports to be connected directly to the tunable OTs.
OTs : optical transponders , so now we can connect the tunable transponders directly to the TOADM ( CLS ports ) for wavelengths routing and forwarding.
CLS : colorless Ports.
It has also port THRU , which can be used to connect 2 CWRs together to extend the number of degrees.
LinkedIn: ![]()