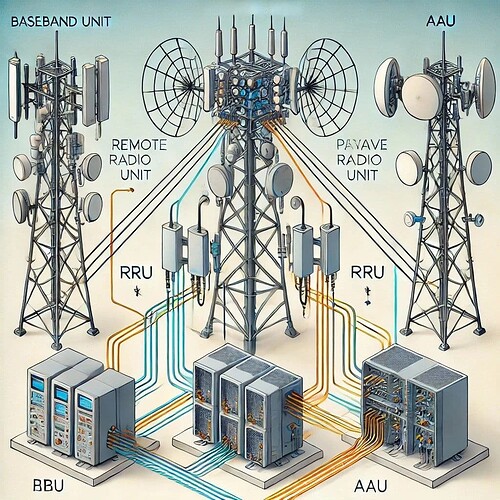
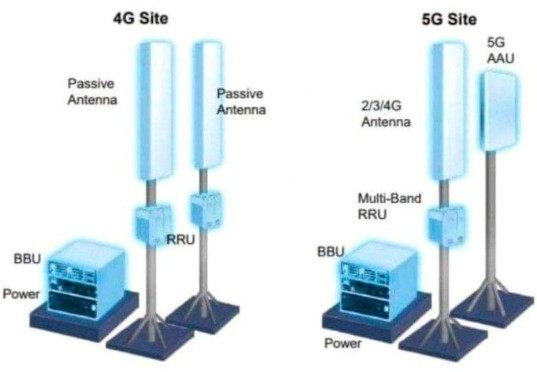
AAU, RRU, and BBU are key components in a telecom network, particularly in modern wireless communication systems like 4G and 5G. Here’s a breakdown of each:
BBU (Baseband Unit)
- The central processing unit in a base station.
- Handles baseband signal processing, transmission scheduling, and network interfacing.
- Usually located in a data center or at the base of a cell tower.
- Connected to the RRU or AAU via fiber optic cables.
RRU (Remote Radio Unit)
- Converts digital signals from the BBU into radio signals and vice versa.
- Mounted near the antenna to reduce signal loss.
- Helps in improving network efficiency by reducing transmission distances.
AAU (Active Antenna Unit)
- Integrates the RRU and antenna into a single unit.
- Used mainly in 5G networks to support massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output).
- Enhances signal strength and coverage, reducing the need for separate RRUs.
Here is a technical diagram comparing AAU, RRU, and BBU in a telecom network. It visually represents their placement and connectivity in a network setup.
LinkedIn: ![]()