-
Best Effort follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle.
-
Best Effort has no traffic prioritization and serves as the default QoS mechanism.
-
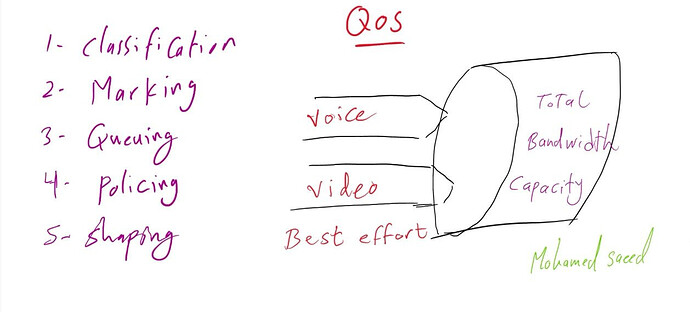
QoS (Quality of Service) optimizes network resources to enhance data transmission and prioritize traffic based on type.
-
Classification categorizes traffic by type and importance, such as voice, video, and data.
-
Marking involves adding labels to packets based on their type.
-
Queuing determines how an output interface processes and forwards traffic.
-
Common Queue Types:
- LLQ (Low Latency Queue): Ensures low delay for high-priority traffic.
- CB-WFQ (Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing): Allocates bandwidth fairly based on traffic classification.
- Policing drops packets exceeding the CIR (Committed Information Rate).
- Shaping buffers excess packets over the CIR instead of dropping them immediately.
- CIR (Committed Information Rate): The minimum guaranteed bandwidth a network provider commits to under normal conditions.
- RTP (Real-Time Protocol): Used for transmitting voice and video traffic.
- Header Compression reduces a 10-40 byte header to 1 byte, especially useful for low-speed links.
LinkedIn: ![]()