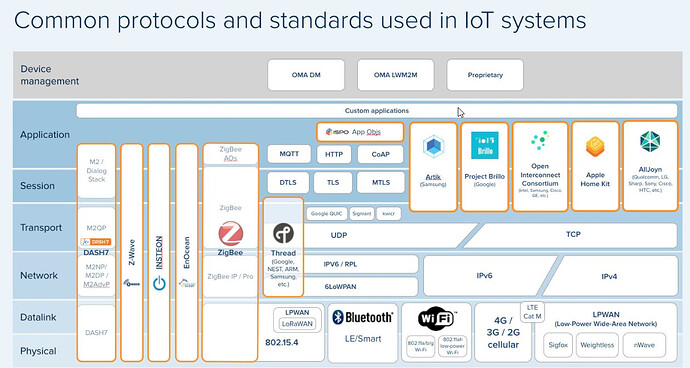
There are several protocols and standards commonly used in 𝐈𝐨𝐓 systems to ensure interoperability, secure communication, and efficient data exchange as defined in the Infographic. Here are some of the key ones:
-
𝐌𝐐𝐓𝐓 (𝐌𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐐𝐮𝐞𝐮𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐓𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐫𝐲 𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭):
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for efficient communication between IoT devices and the server or cloud. It follows a publish-subscribe model, allowing devices to publish data to topics and other devices or applications to subscribe to those topics to receive the data. -
𝐇𝐓𝐓𝐏 (𝐇𝐲𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐱𝐭 𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐟𝐞𝐫 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐥):
HTTP is a widely used protocol for communication between web browsers and servers. In the context of IoT, HTTP is often used for device management, configuration, and data retrieval. -
𝐂𝐨𝐀𝐏 (𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐝 𝐀𝐩𝐩𝐥𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐥):
CoAP is a lightweight application-layer protocol designed for constrained devices and networks, such as those found in IoT deployments. -
𝐀𝐌𝐐𝐏 (𝐀𝐝𝐯𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐌𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐐𝐮𝐞𝐮𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐭𝐨𝐜𝐨𝐥):
AMQP is a messaging protocol that enables reliable and secure communication between devices and applications. It supports asynchronous, message-oriented communication patterns and provides features such as message queuing, routing, and transaction management. -
𝐙𝐢𝐠𝐛𝐞𝐞:
Zigbee is a low-power wireless communication protocol specifically designed for IoT devices. -
𝐙-𝐖𝐚𝐯𝐞:
Z-Wave is a wireless communication protocol primarily used for home automation and smart home applications. It operates in the sub-GHz frequency band and offers low power consumption, long-range coverage, and mesh networking capabilities. -
𝐋𝐨𝐑𝐚𝐖𝐀𝐍:
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, wide-area networking protocol designed for long-range communication with low-power IoT devices. It enables devices to communicate wirelessly over long distances while conserving battery life. -
𝐎𝐏𝐂 𝐔𝐀 (𝐎𝐏𝐂 𝐔𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐞𝐝 𝐀𝐫𝐜𝐡𝐢𝐭𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞):
OPC UA is a widely adopted industrial communication protocol for machine-to-machine communication in industrial IoT systems. It provides a secure and scalable framework for interoperability between devices, machines, and industrial software systems.
These protocols and standards play a crucial role in enabling seamless communication, interoperability, and security within IoT systems. The specific protocols used in an IoT deployment depend on factors such as the application domain, device capabilities, network infrastructure, and specific requirements of the system.
Source: ![]()