In Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (hashtag#DWDM) systems, two major types of dispersion affect signal integrity over long distances. In this post we will simply explain the Chromatic Dispersion:-
-
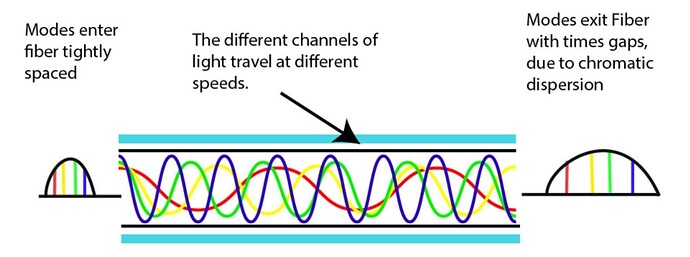
Definition: Chromatic dispersion occurs because different wavelengths of light travel at slightly different speeds through an optical fiber. In DWDM, where multiple wavelengths (channels) are closely spaced and transmitted simultaneously, this dispersion leads to pulse broadening, making it harder to distinguish between ones and zeros.
-
Types:
• Material dispersion: Caused by the wavelength dependence of the refractive index of the fiber material.
• Waveguide dispersion: Due to the fiber structure and how the mode propagates in the core vs. cladding. -
Effects:
• Pulse spreading over long distances.
• Inter-symbol interference (ISI).
• Channel overlap in high data rate systems. -
Mitigation Techniques in DWDM:
• Dispersion-Compensating Fiber (DCF)
• Fiber Bragg Gratings
• Electronic Dispersion Compensation (EDC)
• Advanced modulation formats (e.g., coherent detection)
LinkedIn: ![]()