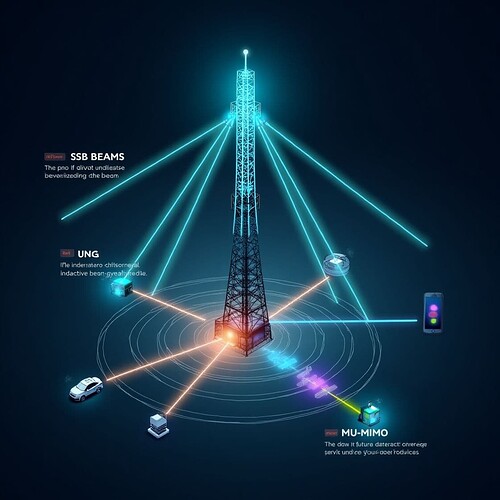
Ever wondered how 5G networks deliver such high speeds and reliable connectivity to so many users at once?
The secret lies in advanced beamforming techniques - both static and dynamic - working hand-in-hand with Synchronization Signal Block (SSB) and Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO).
![]() Static Beamforming (SSB):
Static Beamforming (SSB):
- When you power on your 5G device, the network first uses static or semi-static beams - like those in SSB - to broadcast synchronization signals.
- These fixed beams sweep across the cell, allowing your device to find and connect to the strongest signal.
- It’s the initial handshake that gets you onto the network.
![]() Dynamic Beamforming:
Dynamic Beamforming:
- Once connected, the magic of dynamic beamforming kicks in.
- The network continuously adapts and steers beams in real time, optimizing coverage and throughput for each user.
- This is especially crucial for users on the move or in crowded environments.
![]() Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO):
Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO):
- Dynamic beamforming is the backbone of MU-MIMO, enabling the network to serve multiple users simultaneously on the same channel by directing separate, optimized beams to each user.
- This dramatically increases network capacity and efficiency.
![]() The Big Picture:
The Big Picture:
- Static beamforming (SSB) gets users connected, while dynamic beamforming powers efficient, high-capacity data transmission and enables MU-MIMO.
- Together, they make 5G networks faster, more reliable, and ready for the future.
LinkedIn: ![]()