All PONs lead to faster fiber.
But not all take the same route.
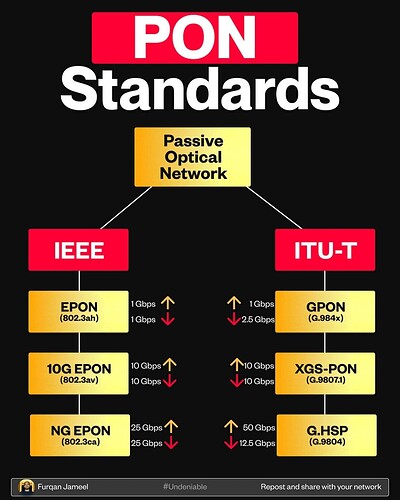
Passive Optical Networks (PONs) come in two major flavors:
IEEE and ITU-T.
Same goal—fiber-based broadband.
Different paths, standards, and speeds.
Let’s break it down:
![]() IEEE Side
IEEE Side
EPON (802.3ah)
![]() 1 Gbps upstream
1 Gbps upstream
![]() 1 Gbps downstream
1 Gbps downstream
10G EPON (802.3av)
![]() 10 Gbps upstream
10 Gbps upstream
![]() 10 Gbps downstream
10 Gbps downstream
NG EPON (802.3ca)
![]() 25 Gbps upstream
25 Gbps upstream
![]() 25 Gbps downstream
25 Gbps downstream
![]() ITU-T Side
ITU-T Side
GPON (G.984x)
![]() 1 Gbps upstream
1 Gbps upstream
![]() 2.5 Gbps downstream
2.5 Gbps downstream
XGS-PON (G.9807.1)
![]() 10 Gbps upstream
10 Gbps upstream
![]() 10 Gbps downstream
10 Gbps downstream
G.HSP (G.9804)
![]() 50 Gbps upstream
50 Gbps upstream
![]() 12.5 Gbps downstream
12.5 Gbps downstream
Higher speed doesn’t always mean better.
Balance matters more.
Some standards prioritize upload.
Others favor downloading.
Each fits different broadband needs—rural, urban, enterprise, or home.
Choose based on need, not just numbers.
Because in fiber, what’s fast must also be right.
Thanks for reading.
LinkedIn: ![]()