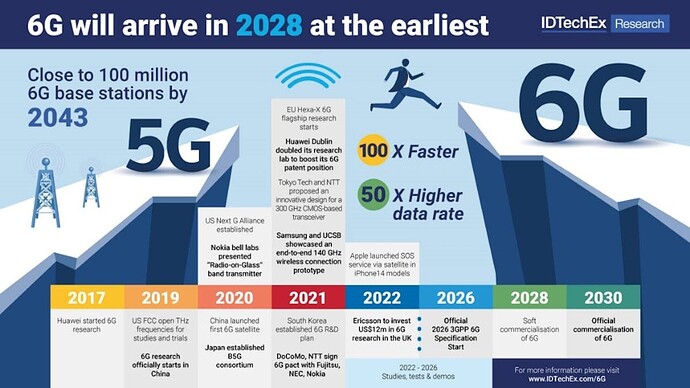
5G is still in its early stages of deployment, but the next generation of wireless technology is already on the horizon.
6G, or sixth-generation wireless, is expected to offer significant improvements over 5G in terms of speed, latency, and capacity.
One of the key goals of 6G is to achieve ultra-high data rates. Current 5G networks can support data rates of up to 100 gigabits per second (Gbps), but 6G is expected to reach speeds of up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps). This would be enough to download a full HD movie in just a few seconds.
Another key goal of 6G is to reduce latency. Latency is the time it takes for a signal to travel from one point to another. 5G networks have latency of around 1 millisecond, but 6G is expected to achieve latency of just one microsecond. This would make it possible for real-time applications such as remote surgery and autonomous driving to be used on a widespread basis.
In addition to speed and latency, 6G is also expected to offer significant improvements in capacity. 5G networks can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, but 6G is expected to support up to 100 million devices per square kilometer. This would allow for a much greater number of devices to be connected to the network simultaneously.
6G is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work. With its ultra-high speeds, low latency, and massive capacity, 6G will enable new applications and services that are simply not possible with today’s technology.
What are the potential benefits of 6G technology?
The potential benefits of 6G technology are vast. Some of the most promising applications include:
-
Ultra-high-definition (UHD) video streaming: 6G will enable the streaming of UHD video with no buffering or lag.
-
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): 6G will provide the bandwidth and low latency needed for immersive VR and AR experiences. This will open up new possibilities for gaming, education, and training.
-
Remote surgery: 6G will make it possible for surgeons to perform surgery remotely. This will allow doctors to operate on patients in remote locations, even in developing countries.
-
Autonomous vehicles: 6G will provide the connectivity and low latency needed for autonomous vehicles to operate safely. This will revolutionize the transportation industry and make it possible for self-driving cars to become a reality.
What are the challenges of 6G technology?
Some of the most significant challenges include:
-
Spectrum availability: 6G will require new spectrum to achieve its full potential. This spectrum is not currently available, and there is a need for international cooperation to allocate it.
-
Security: More complex and sophisticated network than 5G. This will make it more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
-
Cost: More expensive to deploy than 5G. This could limit its adoption in developing countries.
LinkedIn: ![]()