![]() Layer 1 (Physical Layer - L1)
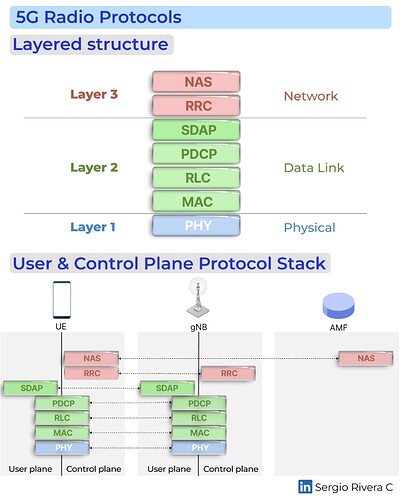
Layer 1 (Physical Layer - L1)
Main functions: Handles wireless transmission, modulation, coding, and signal processing.
Protocols:
![]() PHY (Physical Layer): handles the transmission and reception of raw data over the air, including power control, synchronization, random access, and HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request).
PHY (Physical Layer): handles the transmission and reception of raw data over the air, including power control, synchronization, random access, and HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request).
![]() Layer 2 (Data Link Layer - L2)
Layer 2 (Data Link Layer - L2)
Main functions: Ensures reliable data transfer, error correction, and efficient resource allocation.
Protocols:
![]() MAC (Medium Access Control): Manages radio resource allocation and scheduling.
MAC (Medium Access Control): Manages radio resource allocation and scheduling.
![]() RLC (Radio Link Control): Provides segmentation, reassembly, and retransmission of data packets.
RLC (Radio Link Control): Provides segmentation, reassembly, and retransmission of data packets.
![]() PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol): Handles data compression, encryption, and integrity protection.
PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol): Handles data compression, encryption, and integrity protection.
![]() SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol): maps 5G core network QoS flows to data radio bearers for QoS (Quality of Service) purposes. Used only for 5G SA (Standalone).
SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol): maps 5G core network QoS flows to data radio bearers for QoS (Quality of Service) purposes. Used only for 5G SA (Standalone).
![]() Layer 3 (Network Layer - L3)
Layer 3 (Network Layer - L3)
Main functioins: Manages connections, mobility, and security between devices and the core network.
Protocols:
![]() RRC (Radio Resource Control): Manages connection setup, handovers, mobility, and security.
RRC (Radio Resource Control): Manages connection setup, handovers, mobility, and security.
![]() NAS (Non-Access Stratum): Facilitates communication between the UE and the 5G Core, handling authentication, session management, and mobility across different network nodes.
NAS (Non-Access Stratum): Facilitates communication between the UE and the 5G Core, handling authentication, session management, and mobility across different network nodes.
Shown in the image:
The separation of User Plane and Control Plane functions across the protocol stack, a key concept in 5G architecture.
Understanding this layered structure is fundamental for anyone working in RAN, Open RAN or Core.
![]() Related content:
Related content:
Article: 5G Radio Protocols: A Quick Structural Guide
LinkedIn: ![]()