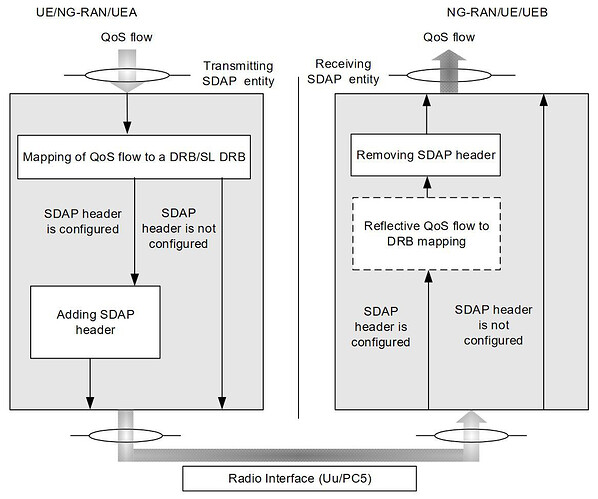
![]() 5G NR has introduced a new sublayer, SDAP, in the air-interface protocols stack at both the UE and gNB sides to manage QoS through QoS flows.
5G NR has introduced a new sublayer, SDAP, in the air-interface protocols stack at both the UE and gNB sides to manage QoS through QoS flows.
![]() The SDAP layer is the topmost L2 sublayer at 5G NR protocol stack SA where gNB connects to 5G Core network.
The SDAP layer is the topmost L2 sublayer at 5G NR protocol stack SA where gNB connects to 5G Core network.
![]() SDAP is only applicable to the SA option.
SDAP is only applicable to the SA option.
![]() SDAP sublayer exists only in the user plane in both gNB and UE.
SDAP sublayer exists only in the user plane in both gNB and UE.
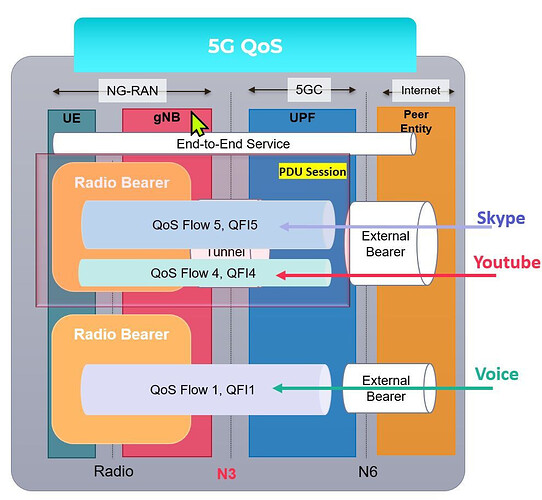
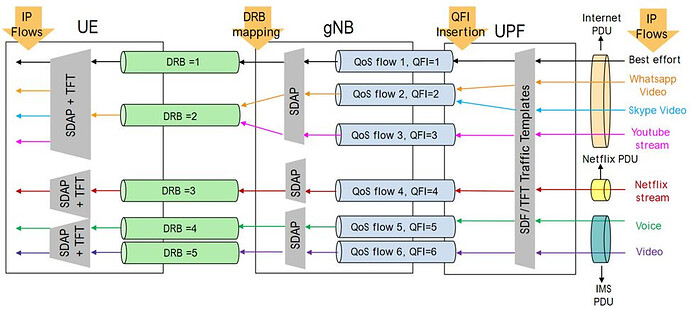
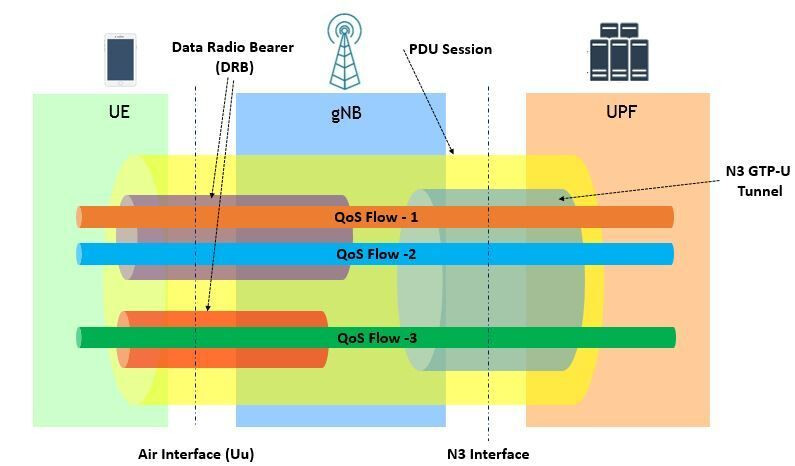
![]() SDAP interfaces to 5GC UPF using NG-U interface via QoS flows and to the PDCP lower layer via Data Radio Bearers (DRBs).
SDAP interfaces to 5GC UPF using NG-U interface via QoS flows and to the PDCP lower layer via Data Radio Bearers (DRBs).
![]() It is essential role is to map traffic from QoS flows to suitable DRBs.
It is essential role is to map traffic from QoS flows to suitable DRBs.
![]() SDAP layer doesn’t exist in LTE since QoS flows were introduced only in 5G.
SDAP layer doesn’t exist in LTE since QoS flows were introduced only in 5G.
![]() Functions of SDAP:mobile_phone_with_arrow:
Functions of SDAP:mobile_phone_with_arrow:
![]() QoS Management: SDAP enables the mapping of different QoS flows to appropriate data paths. This helps ensure that specific services receive the required bandwidth and latency, enhancing user experience.
QoS Management: SDAP enables the mapping of different QoS flows to appropriate data paths. This helps ensure that specific services receive the required bandwidth and latency, enhancing user experience.
![]() Packet Processing: It processes user data packets, allowing for differentiation between various services. It can classify and prioritize packets based on their QoS requirements.
Packet Processing: It processes user data packets, allowing for differentiation between various services. It can classify and prioritize packets based on their QoS requirements.
![]() Flow Control: It manages the flow of data by enabling the control of how much data is sent over the network. This is essential for maintaining the performance of high-priority applications.
Flow Control: It manages the flow of data by enabling the control of how much data is sent over the network. This is essential for maintaining the performance of high-priority applications.
![]() PDU Session Establishment and Modification: It is involved in the establishment and modification of PDU sessions. PDU sessions are logical connections that carry user data between the UE and the 5G core network.
PDU Session Establishment and Modification: It is involved in the establishment and modification of PDU sessions. PDU sessions are logical connections that carry user data between the UE and the 5G core network.
![]() Support for Multiple QoS Flows: It supports the multiplexing of multiple QoS flows over a single data connection, which is essential for efficiently utilizing network resources.
Support for Multiple QoS Flows: It supports the multiplexing of multiple QoS flows over a single data connection, which is essential for efficiently utilizing network resources.
![]() UPF Interaction: It interacts with the User Plane Function (UPF), which is responsible for processing and forwarding user plane data. SDAP communicates with UPF to convey QoS-related information and ensure proper adaptation.
UPF Interaction: It interacts with the User Plane Function (UPF), which is responsible for processing and forwarding user plane data. SDAP communicates with UPF to convey QoS-related information and ensure proper adaptation.
![]() Interworking with Legacy Systems: SDAP provides mechanisms for interoperability with previous generations of mobile networks (like 4G), facilitating smooth transitions and coexistence in mixed-environment scenarios.
Interworking with Legacy Systems: SDAP provides mechanisms for interoperability with previous generations of mobile networks (like 4G), facilitating smooth transitions and coexistence in mixed-environment scenarios.
![]() Interaction with N4 Interface: SDAP interacts with the N4 interface, which connects the UPF and the SMF, facilitating the exchange of information related to user plane data handling.
Interaction with N4 Interface: SDAP interacts with the N4 interface, which connects the UPF and the SMF, facilitating the exchange of information related to user plane data handling.
![]() SDAP Benefits
SDAP Benefits
![]() Enhanced User Experience: By effectively managing QoS, SDAP helps ensure that applications such as video streaming, gaming, and IoT services perform optimally.
Enhanced User Experience: By effectively managing QoS, SDAP helps ensure that applications such as video streaming, gaming, and IoT services perform optimally.
![]() Enhanced QoS Management: SDAP enables precise management of QoS flows, ensuring that different types of traffic receive appropriate bandwidth, latency, and reliability based on their specific requirements.
Enhanced QoS Management: SDAP enables precise management of QoS flows, ensuring that different types of traffic receive appropriate bandwidth, latency, and reliability based on their specific requirements.
![]() Resource Efficiency: The protocol optimizes the use of network resources, contributing to the overall efficiency and capacity of 5G networks.
Resource Efficiency: The protocol optimizes the use of network resources, contributing to the overall efficiency and capacity of 5G networks.
LinkedIn: ![]()