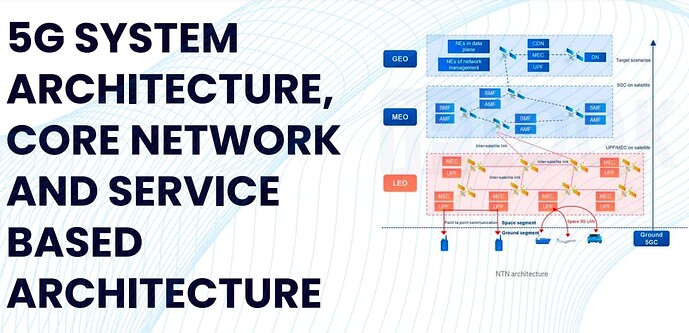
Did you know that 5G networks are not just limited to cell towers on the ground? With Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN), satellites are now becoming a key part of 5G, bringing connectivity to remote areas, oceans, and even airplanes
Here’s a simple breakdown of how 5G and NTN work together:
Two Ways Satellites Can Work in 5G
- Transparent Mode (Bent-Pipe) : The satellite only forwards signals like a mirror in the sky. This is already standardized and works today.
- Regenerative Mode : The satellite processes signals onboard, reducing delays and improving performance. This is still under study and will be part of future 5G updates.
Challenges of Using Satellites in 5G
- High Latency : Unlike regular 5G towers, satellites are far away, so signals take longer to travel, especially with GEO satellites (1000+ ms delay).
- Quality of Service (QoS) : 5G adjusts how it prioritizes traffic for satellites (buffering videos can handle delays, but live calls need faster connections).
- Cross-Border Coverage : Since satellites cover multiple countries, networks must manage connections properly to follow regulations.
Future of NTN in 5G
- Faster & Smarter Satellites : Future Regenerative Mode satellites will help reduce delays.
- Better Connectivity Everywhere : Dual connectivity between ground towers + satellites will ensure seamless switching when moving between coverage areas.
- More Advanced Services : NTN will help connect IoT devices, ships, aircraft, and even future space missions
You can find my full article below, where I explain in detail how NTN integrates with 5G, its challenges, and future advancements ![]()
That’s it ![]()
Eng Alali khalaf
PDF: ![]() 5G NTN Architecture (by Alali Khalaf).pdf (5.5 MB)
5G NTN Architecture (by Alali Khalaf).pdf (5.5 MB)
LinkedIn: ![]()