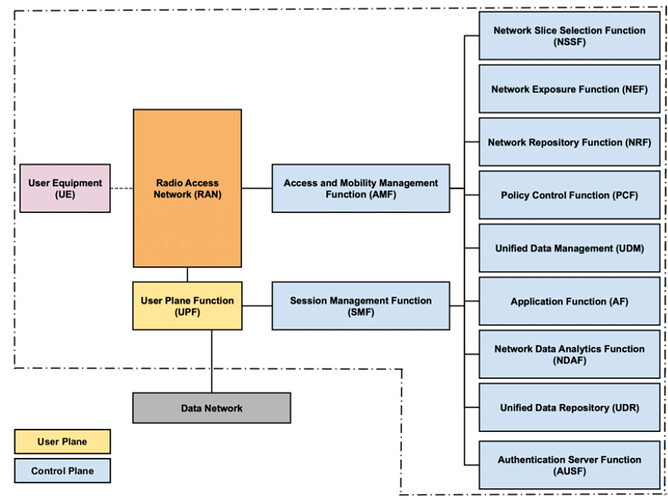
5G network architecture is a complex system of interconnected components designed to support the high-speed, low-latency, and massive machine-to-machine communication requirements of the fifth-generation mobile network. The architecture consists of several layers, including the radio access network (RAN), the core network, and the user equipment (UE).
Radio Access Network (RAN):
The RAN is responsible for managing the wireless connections between the user equipment and the core network. It comprises of the main components:
-
gNB (5G New Radio Base Station): responsible for wireless communication with user equipment
-
ng-eNB (Next Generation Enhanced NodeB): Acts as an interface for 5G network
The CORE network is responsible for managing the user data and providing services to the user equipment. It comprises of three main components:
- AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function): responsible for managing user authentication, mobility, and security functions.
- UPF (User Plane Function): responsible for routing and forwarding user data packets.
- SMF (Session Management Function): responsible for managing user sessions and Quality of Service (QoS) requirements.
The UE refers to the devices that connect to the 5G network, such as smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices.
- User Equipment (UE):
Overall, 5G network architecture is designed to provide faster speeds, lower latency, and improved reliability compared to previous generations of mobile networks. It enables new use cases such as massive IoT, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery, which require low latency, high bandwidth, and high reliability connections.
Credits: ![]()