Mastering 5G: Definitions, Applications, Benefits, and Examples
Want to understand 5G technology in a simple yet powerful way?
5G is revolutionizing connectivity, speed, and real-time applications, making it essential for tech professionals to grasp its core concepts.
Here’s a breakdown of the most important 5G concepts, their applications, and benefits:
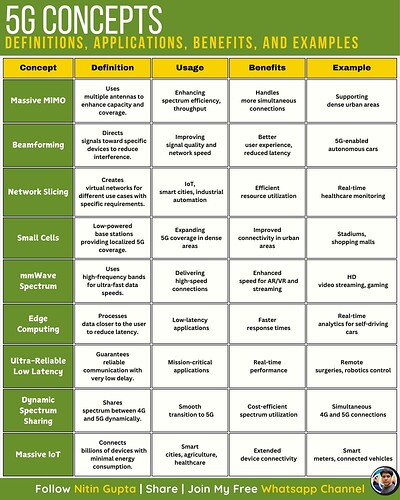
- Massive MIMO
 Uses multiple antennas to boost capacity.
Uses multiple antennas to boost capacity.
 Benefit: Supports more simultaneous connections.
Benefit: Supports more simultaneous connections.
 Example: Helps in dense urban areas.
Example: Helps in dense urban areas. - Beamforming
 Directs signals precisely to reduce interference.
Directs signals precisely to reduce interference.
 Benefit: Better user experience & signal strength.
Benefit: Better user experience & signal strength.
 Example: 5G-enabled autonomous cars.
Example: 5G-enabled autonomous cars. - Network Slicing
 Creates virtual networks for specific use cases.
Creates virtual networks for specific use cases.
 Benefit: More efficient resource allocation.
Benefit: More efficient resource allocation.
 Example: Real-time healthcare monitoring.
Example: Real-time healthcare monitoring. - Small Cells
 Low-powered base stations boost coverage.
Low-powered base stations boost coverage.
 Benefit: Enhanced connectivity in urban areas.
Benefit: Enhanced connectivity in urban areas.
 Example: Stadiums & shopping malls.
Example: Stadiums & shopping malls. - mmWave Spectrum
 High-frequency bands for ultra-fast data.
High-frequency bands for ultra-fast data.
 Benefit: Ideal for AR/VR, HD streaming, and gaming.
Benefit: Ideal for AR/VR, HD streaming, and gaming.
 Example: HD video streaming.
Example: HD video streaming. - Edge Computing
 Processes data closer to the user.
Processes data closer to the user.
 Benefit: Faster response & real-time processing.
Benefit: Faster response & real-time processing.
 Example: Real-time analytics for self-driving cars.
Example: Real-time analytics for self-driving cars. - Ultra-Reliable Low Latency (URLLC)
 Guarantees minimal network delays.
Guarantees minimal network delays.
 Benefit: Mission-critical operations like remote control.
Benefit: Mission-critical operations like remote control.
 Example: Surgeries & robotics control.
Example: Surgeries & robotics control. - Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)
 Shares spectrum between 4G & 5G dynamically.
Shares spectrum between 4G & 5G dynamically.
 Benefit: Optimized spectrum utilization.
Benefit: Optimized spectrum utilization.
 Example: 4G & 5G co-existence.
Example: 4G & 5G co-existence. - Massive IoT
 Connects billions of IoT devices.
Connects billions of IoT devices.
 Benefit: Extended device connectivity.
Benefit: Extended device connectivity.
 Example: Smart meters & connected vehicles.
Example: Smart meters & connected vehicles.
5G is not just about speed—it’s about connectivity, efficiency, and innovation.
LinkedIn: ![]()