AMF in 5G doesn’t get the headlines.
But without it, 5G would simply fail.
Here’s why it matters.
AMF stands for Access and Mobility Management Function.
It’s one of the key pieces inside a 5G core network.
It handles how devices connect, move, and stay secure.
![]() It acts like a traffic director.
It acts like a traffic director.
![]() It keeps sessions alive when users move.
It keeps sessions alive when users move.
![]() It makes sure authentication is seamless.
It makes sure authentication is seamless.
![]() It talks to every major player in the network.
It talks to every major player in the network.
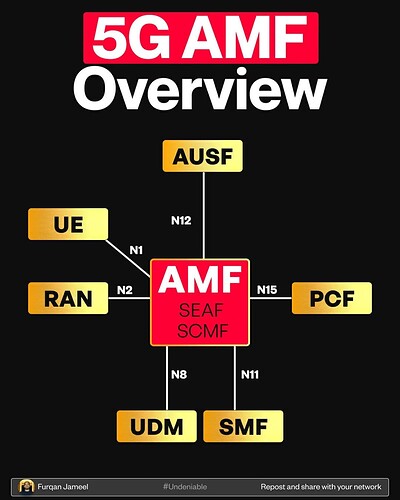
Here’s who the AMF connects to:
- UE (User Equipment) via N1.
- RAN (Radio Access Network) via N2.
- AUSF (Authentication Server) via N12.
- PCF (Policy Control Function) via N15.
- UDM (User Data Management) via N8.
- SMF (Session Management Function) via N11.
Inside AMF, two major roles exist:
![]() SEAF: Security Anchor Function.
SEAF: Security Anchor Function.
SEAF secures the device’s identity and communication.
![]() SCMF: Session Context Management Function.
SCMF: Session Context Management Function.
SCMF maintains the session info as users move across cells.
AMF is not about speed.
It’s about keeping you connected, safely and reliably.
Thanks for reading.
LinkedIn: ![]()