4G Scheduling ![]()
![]()
[What, factors, types, challenges, and optimization]
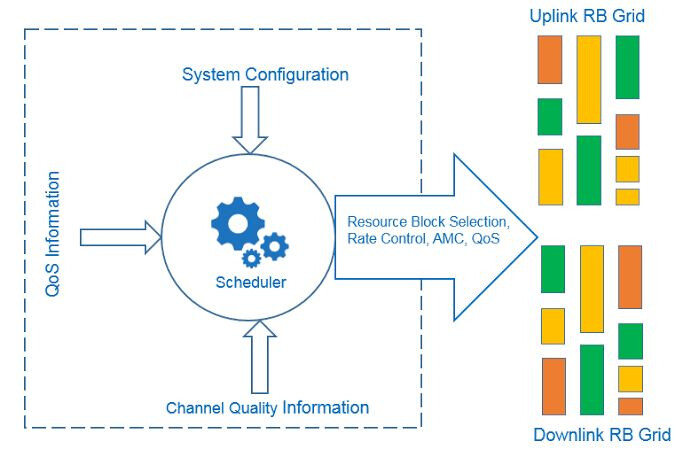
LTE scheduling is the intelligent process of allocating radio resources (time, frequency, and power) to different UEs and services in both UL and DL directions.
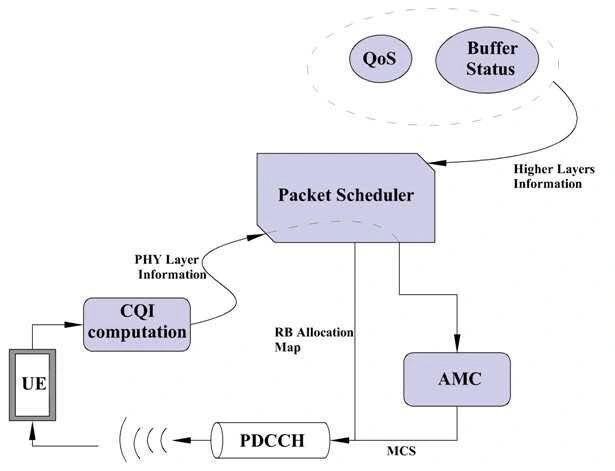
![]() It decides in 1 millisecond and sends it in PDCCH.
It decides in 1 millisecond and sends it in PDCCH.
![]() Scheduling Existing in eNB only.
Scheduling Existing in eNB only.
![]() Factors influencing scheduling…
Factors influencing scheduling…
QoS, CQI, Waiting Time (WT), Buffer Status (BS), User Priority, radio conditions, eNB configurations (power, MIMO, etc.), and available resources.
![]() Scheduling types…
Scheduling types…
![]() Static scheduling (depends on fixed resources).
Static scheduling (depends on fixed resources).
![]() Dynamic scheduling.
Dynamic scheduling.
![]() Semi-persistent scheduling (SPS) (for VoLTE).
Semi-persistent scheduling (SPS) (for VoLTE).
![]() Types of LTE Scheduling Algorithms…
Types of LTE Scheduling Algorithms…
![]() Round Robin (RR): Simple and fairness-focused. Grants resources cyclically to each user. Great for ensuring basic fairness but might not maximize throughput.
Round Robin (RR): Simple and fairness-focused. Grants resources cyclically to each user. Great for ensuring basic fairness but might not maximize throughput.
![]() Proportional Fair (PF): Strikes a balance between fairness and throughput. Prioritizes users with better channel conditions relative to their past throughput. A popular choice for its efficiency.
Proportional Fair (PF): Strikes a balance between fairness and throughput. Prioritizes users with better channel conditions relative to their past throughput. A popular choice for its efficiency.
![]() Enhanced Proportional Fair (EPF): An advanced version of PF, often incorporating QoS, CQI, Waiting Time (WT), and Buffer Status (BS) to make more informed scheduling decisions. Can significantly improve overall network performance.
Enhanced Proportional Fair (EPF): An advanced version of PF, often incorporating QoS, CQI, Waiting Time (WT), and Buffer Status (BS) to make more informed scheduling decisions. Can significantly improve overall network performance.
![]() Maximum Carrier to Interference Ratio (Max C/I): Throughput centric. Prioritizes users with the best instantaneous channel quality (highest CQI) to maximize cell throughput. This may lead to some fairness problems.
Maximum Carrier to Interference Ratio (Max C/I): Throughput centric. Prioritizes users with the best instantaneous channel quality (highest CQI) to maximize cell throughput. This may lead to some fairness problems.
![]() Challenges in LTE Scheduling…
Challenges in LTE Scheduling…
![]() Dynamic Channel Conditions: require fluctuating signal strength and interference require schedulers to be highly adaptive.
Dynamic Channel Conditions: require fluctuating signal strength and interference require schedulers to be highly adaptive.
![]() Diverse QoS Requirements: From voice (VoLTE) to video streaming to IoT, each service has unique latency, bandwidth, and reliability needs.
Diverse QoS Requirements: From voice (VoLTE) to video streaming to IoT, each service has unique latency, bandwidth, and reliability needs.
![]() Fairness vs. Efficiency Trade-off: Balancing the need to serve all users fairly while maximizing overall network capacity.
Fairness vs. Efficiency Trade-off: Balancing the need to serve all users fairly while maximizing overall network capacity.
![]() Complexity and Real-time Operation: Schedulers must make decisions in 1 millisecond, demanding efficient algorithms and robust implementation.
Complexity and Real-time Operation: Schedulers must make decisions in 1 millisecond, demanding efficient algorithms and robust implementation.
![]() Optimization Strategies…
Optimization Strategies…
![]() Advanced Algorithm Design: Continuously refining algorithms like EPF to better adapt to varying network conditions and user demands.
Advanced Algorithm Design: Continuously refining algorithms like EPF to better adapt to varying network conditions and user demands.
![]() CQI Feedback Mechanisms: Accurate and timely CQI reporting is crucial for effective link adaptation and scheduling decisions.
CQI Feedback Mechanisms: Accurate and timely CQI reporting is crucial for effective link adaptation and scheduling decisions.
![]() QoS Aware Scheduling: Implementing sophisticated mechanisms to prioritize traffic based on QoS Class Identifiers (QCIs) and service requirements.
QoS Aware Scheduling: Implementing sophisticated mechanisms to prioritize traffic based on QoS Class Identifiers (QCIs) and service requirements.
![]() Dynamic Resource Allocation: Flexibly adjusting resource allocation based on real-time traffic patterns and network load.
Dynamic Resource Allocation: Flexibly adjusting resource allocation based on real-time traffic patterns and network load.
LinkedIn: ![]()