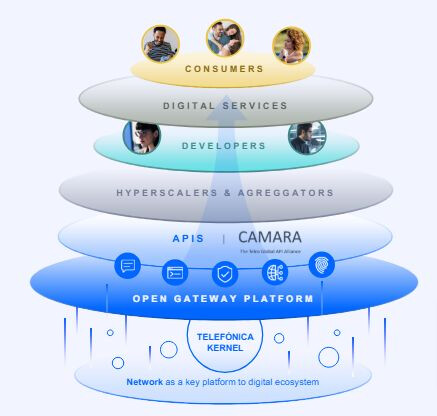
Understand end-to-end ecosystem of telecom network APIs and the role of each participating layer, like end consumers, digital services, developers, hyperscalers & aggregators:
David del Val of Telefónica at MWC 2024 - This is an important explanation of GSMA Open Gateway and the end-to-end ecosystem of telecom network APIs and the role of each participating layer, like end consumers, digital services, developers, hyperscalers & aggregators, CAMARA Project APIs, and the Open Gateway (on top of the Telefonica kernel).
Everything is software. Everybody is writing in applications, and applications are using the capabilities of other platforms to build bigger applications, more performing, and faster time. Telos has many capabilities in our networks, in our CRM systems, and in all the data that we have about our customers. But until today, it was impossible for developers to use that information and data, and that’s precisely what Open Gateway is changing.
If we look at how Open Gateway looks, we have consumers and businesses that need to solve some problems; they have a pain point. There are digital services, applications, and all kinds of software that are solving these needs for customers. Who is writing this software? Of course, developers.
Developers need simplicity; they need to work in the environments that they know, like AWS, Google, or Azure. They do that all the time. They also need that when they call an API to get a capability from a Telco, they only need to develop the software once, call the API, and it works for all the Telos.
That’s where the aggregation function comes into play. Companies like Vonage or Infobip are providing this aggregation function so that you call once, and it works in all the Telos. For that to happen, as we see in the figure, you have the hyperscalers and aggregators. These hyperscalers and aggregators have to integrate with 700 Telos around the world. That’s an impossible task unless all the Telos expose the same layer, the same interface, and the same plug, and that’s what Open Gateway is.
This interface is the CAMARA APIs. CAMARA Project is a standard body, open-source, in collaboration with the GSMA and The Linux Foundation that offers these APIs so that all Telos expose the same so that hyperscalers and aggregators can expose that to the developers. The magic happens below the CAMARA APIs. You need a platform in each of the Telos to expose these APIs following this standard. In the case of Telefónica, we’re lucky because we have Telefonica Kernel, which is a platform that abstracts all the complexity underneath our network in our different countries (in Brazil, in Germany, in Argentina, everywhere) and exposes the APIs as a single API to the aggregator so that they can aggregate and expose it to the developer who builds the solutions with software.
So this is GSMA Open Gateway, in a nutshell.
LinkedIn: ![]()